Databases Reference
In-Depth Information
to be audited, and the where clause examines updates (or deletes) of the al-
lergy information in patient Charles's medical record. The before and after
images of updated tuples can be accessed using special
before
and
after
key-
words. The audit returns the identities of logged commands having performed
modifications that qualify the audit expression. The command log records all
queries and commands submitted to the database along with annotations
such as the identity of the user submitting the query, the time the query was
submitted, and the purpose of the query (if available). Upon receiving the
audit expression above, the system reveals that Dr. Roberts deleted Charles's
allergy information in September, shortly after the patient's death. The hos-
pital can then initiate similar audits to determine whether any information
was modified regarding the patient's test results and to determine whether
Dr. Roberts improperly deleted or modified information in any other patient
records.
Currently, only the high-level design of HDB curation auditing has been
articulated. Deeper technical and implementation issues are topics for further
research.
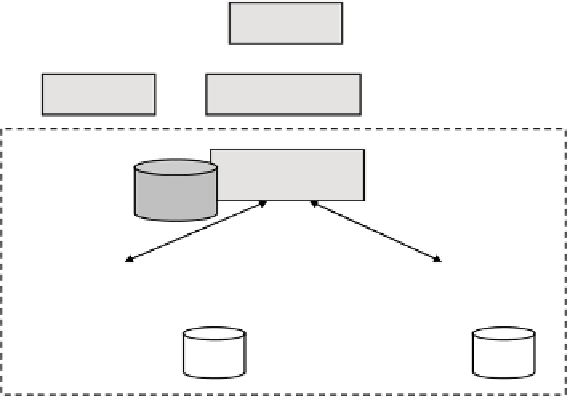
3.3 Sovereign Information Integration
Another enabling technology of a Hippocratic database, called Sovereign In-
formation Integration (SII), allows secure information sharing among multiple
autonomous databases without using a trusted third party [13].
User
Application
Developer
Application
SII Platform
SII Client
Client
Metadata
SII Server 1
SII Server n
. . .
Data
Pr
o
vider (DP)
Data
Pro
v
ider (DP)
Application
Metadata
Application
Metadata
DP DB
DP DB
Fig. 6.
Sovereign Information Integration Architecture