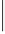Databases Reference
In-Depth Information
r
1
r
2
r
3
r
4
∅
r
1
r
2
r
3
r
1
r
2
r
4
r
1
r
3
r
4
r
2
r
3
r
4
!
!
!
!
!
A
B
C
D
AC
BC
AD
r
1
r
2
r
1
r
3
r
1
r
4
!
!
!
!
!
r
2
r
3
r
2
r
4
r
3
r
4
AB
BD
CD
ACD
BCD
ABD
r
1
r
2
r
3
r
4
"
ABC
#
#
#
#
#
∅
(b)
ABCD
(a)
Fig. 7.
An example of
UH
(a) and
RH
(b)
, and contains 2
|U|
items, and
(i.e., the set of all subsets of
U
)of
U
is defined
as the set containment relation, that is,
∀
a, b
∈
P
(
U
),
a
b
if and only if
b
a
. Each vertex
v
i
in
UH
is associated with a private key
k
i
.Eachuser
u
i
∈U
⊆
is then communicated key
k
i
associated with the vertex representing
the singleton set
. Each resource
r
j
is instead encrypted with the key
k
j
associated with the vertex representing its
acl
. Since partial order relation
{
u
i
}
is defined on the basis of the set containment relation, any user in the
system, by knowing the key of vertex
, can derive all and only the keys
of vertexes representing sets of users including
u
i
. Figure 7(a) represents the
user hierarchy suitable for the access matrix in Fig. 6. To correctly enforce
the given access control policy,
r
1
is encrypted with the key of vertex
ABC
,
r
2
with the key of vertex
ABD
,
r
3
with the key of vertex
CD
,and
r
4
with the
keyofvertex
A
. Due to this key assignment, any user can access exactly the
resources in her capability list. As an example, with respect to the hierarchy
in Fig. 7(a), it is easy to see that
B
can derive the key associated with vertexes
AB
and
BD
that in turn can be used for deriving the keys associated with
vertexes
ABC
and
ABD
, this allowing to access
r
1
and
r
2
, respectively.
In a dual way, it is possible to build a key derivation hierarchy on the
basis of the resources in the system. A
resource-based hierarchy
, denoted
RH
,
is defined as a pair (
P
(
{
u
i
}
R
)
,
), where
P
(
R
) represents the powerset of
R
,and
b
.
To correctly enforce the given policy, each user
u
i
is assigned the key of the
vertex representing her capability list, while each resource
r
j
is encrypted with
the key of the vertex representing the singleton set
is a partial order relation such that
∀
a, b
∈
P
(
R
),
a
b
if and only if
a
⊆
. Considering again the
access matrix in Fig. 6, the corresponding resource hierarchy is represented
in Fig. 7(b).
Although both the models presented for defining a key derivation hierarchy
correctly enforce the access control policy defined by the owner, there is an
important difference that should be considered when deciding which structure
to adopt. As a matter of fact,
UH
allows resources to share the same encryp-
tion key, while each user has her secret key. By contrast, when adopting
RH
,
{
r
j
}