Databases Reference
In-Depth Information
mark
user
usability metric
plugin A
evaluate
key
usability
metrics
plugin
handler
WM
usability metric
plugin B
attributes
alteration rollback log
usability metric
plugin C
JDBC
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
DBMS
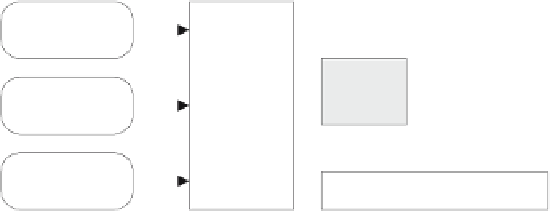
Fig. 10.
Overview of the
wmdb.*
package.
silient to random alterations and uninformed alteration attacks. This is due to
its distribution-based encoding which can naturally survive such alterations.
For example, altering the
entire
watermarked data set within 1% of its original
values only yields a distortion of less than 5% in the detected watermark.
The authors also propose a set of improvements and discuss several prop-
erties of the solutions.
•
Embedding Optimizations: As the encoding resilience is dependent on a
set of parameters (e.g.,
c
,
subset size
,
v
false
,
v
true
), an automatic fine-
tuning mechanism for searching a near-optimum in this parameter space
is proposed. Additionally, the watermarking process could be trained to be
resilient to a set of transformations expected from any potential attacker.
•
Blind Watermarking: The method does not require the availability of the
un-watermarked data at detection time.
•
On-the-Fly Updatability: The authors also discuss mechanisms for han-
dling dynamic data updates. Several scenarios of interest are: (i) updates
that add fresh tuples to the already watermarked data set, (ii) updates
that remove tuples from the already watermarked data and (iii) updates
that alter existing tuples.
4 Categorical Types
So far we have explored the issue of watermarking
numeric
relational content.
Another important relational data type to be considered is categorical data.
Categorical data is data drawn from a discrete distribution, often with a finite
domain. By definition, it is either non-ordered (nominal) such as gender or
city, or ordered (ordinal) such as high, medium, or low temperatures. There