Databases Reference
In-Depth Information
Authorized Role/
Org: Delta
Authorized Role/
Org: Delta
T
3
:
Reserve
Ticket
T
5
:
Purchase a
Ticket
bs
T
2
:
Reserve
Ticket
T
6
:
Reserve a
room
T
1
: Enter
Travel Data
bs
T
4
:
Purchase a
Ticket
Authorized Role:
Clerk
Authorized Role/
Org: Continental
Authorized Role/
Org: Sheraton
Authorized Role/
Org: Continental
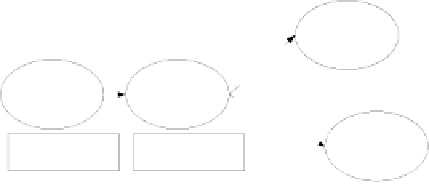
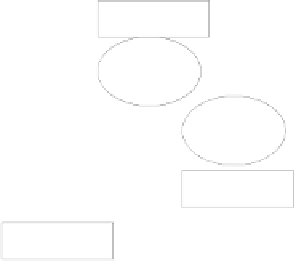
Fig. 5.
Example Inter-organizational Workflow
the execution of
T
2
, Continental must send the remaining workflow to Delta,
based on the outcome of
T
2
. Continental, however, because it has access to the
workflow logic, has knowledge that if it has no ticket or if the ticket costs more
than $400, Delta Airlines may get the business. Knowing this, Continental has
an unfair advantage and may manipulate the price of the ticket, reducing it
just under $400.
Atluri et al. in [4] proposed a decentralized workflow Chinese Wall secu-
rity model to resolve such problems by portioning the workflow in a restrictive
manner. The model uses the notion of self-describing workflows and WFMS
stubs. Self-describing workflows are partitions of a workflow that carry su-
cient information so that they can be managed by a local task execution agent
rather than a central WFMS. A WFMS stub is a light-weight component that
can be attached to a task execution agent, which is responsible for receiving
the self-describing workflow, modifying it and re-sending it to the next task
execution.
Web Services are now being touted as the way to coordinate business enti-
ties in an inter-organizational business process. A Web Service is a collection
of operations that are network-accessible through standardized XML messag-
ing though an interface. In order to created business processes, web services
would need to be combined. However, research on the orchestration of web ser-
vices to form complex business processes is still in its early stages. Research
on determining security policies that should apply to the overall process is
even further behind and is still at the architectural level [22]. Among other
security concerns to address are data privacy, data integrity and audit all of
which become more dicult problems when the organization involved in the
workflow may be unfamiliar to each other, selected by a third party creator
of the overall process. Not only is policy integration needed but languages
and mechanisms for exchanging policy information and information about
those who will participate in the business process still need to be developed.
Kang et al. [20] gave one possible view of how peer-to-peer negotiation of