Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
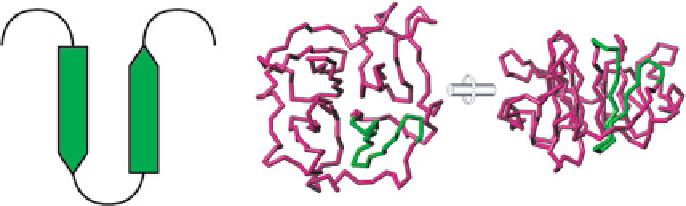
a domain that typically enhances the binding of an MMP to its substrate. SR20 is
highly conserved within MMP12 across species. However, it is not found in other
MMPs. Structural analysis of the MMP12 CTD revealed that SR20 exists in vivo as a
b
-loop (Fig.
9.4
). Since MMP12 CTD is capable of killing bacteria without additional
processing, we were able to identify just three regions of the peptide that could
theoretically interact with bacteria. One of these sequences, KDEK, was of interest
because of its unique composition of two basic residues flanking two acidic ones,
occurring on an exposed loop of the protein. The bactericidal properties of SR20 were
ascribed to these four residues, as mutating this motif and replacing it with the SGRQ
motif found in MMP9, eliminated antimicrobial activity.
MMP12 is the onlyMMP with direct microbicidal activity. Matrilysin (MMP7) is
also essential for host defense against invading pathogens, although in this case, the
antimicrobial properties are indirect (Wilson et al.
1999
). Alpha-defensins are potent
antimicrobial peptides produced by numerous cell types including gastrointestinal
epithelial cells. Upon infection, MMP7 is required to cleave and activate alpha-
defensins prior to their secretion into the extracellular space, where they kill
bacteria. This is the only other report of antimicrobial activity by an MMP. Matri-
lysin is also required for the development of chemotactic gradients that acutely
recruit neutrophils to the lung (Li et al.
2002
). The neutrophil chemokine, KC, is
sequestered within syndecan matrices and requires MMP7 to cleave and release it.
This activity is also important for host defense, as proper neutrophil emigration into
the lung is a major feature of innate host defense against invading microbes.
Neutrophils also possess toxic substances capable of killing invading pathogens,
most notably the reactive oxygen species. Additionally, both CG and NE possess
antimicrobial properties (Gabay et al.
1989
). Based upon results using gene-targeted
mice, it appears that NE plays a greater role than CG in the clearance of bacteria
in vivo.
NE
/
mice display increased mortality when challenged with Gram-
negative infection (Belaaouaj et al.
1998
), which is not observed in
CG
/
mice.
Upon recruitment to sites of acute infection, neutrophils engulf invading patho-
gens. They then shuttle preformed and active NE into the phagolysosomes where it
directly attacks the outer membrane proteins (Omp) located on Gram-negative
S
R
N
L
L
blade IV
exit side
L
L
b
1
b
2
b
3
b
4
b
1
b
2
blade I
V
N
Q
L
F
L
F
K
N
l
L
W
Y
K
90°
L
b
3
b
4
b
2
b
3
S
335
blade III
V
352
blade II
L
b
2
b
3
L
2
3
entry side
b
b
D
E
Fig. 9.4
Macrophage elastase (MMP12) CTD
. Computational three-dimensional model of mouse
MMP12 CTD. The antimicrobial SR-20 sequence is located within CTD blade II including
b
3, as well as the connecting and flanking loops (green trace) (Reproduced
with permission by the author AMH.)
-strands
2 and
b
b