Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Macrophages accumulate in aortic aneurysms as well, where they damage elastic
fibers. The EFs present in human aneurismal tissue also display monocyte chemo-
tactic properties and are likely responsible for the accumulation of macrophages via
chronic progressive elastin destruction (Hance et al.
2002
).
Not all EFs display chemotactic properties. The prototypical EF, VGVAPG, is a
synthetic peptide frequently used in in vitro assays of EF activity (Senior et al.
1984
). Additional study has revealed that essentially all EFs that include the motifs
GXXPG or XGXPG (where X is a hydrophobic amino acid) possess chemotactic
properties (Grosso and Scott
1993a
,
b
). These motifs are highly prevalent in
tropoelastin, the soluble precursor of elastic fibers, representing in excess of 20%
of the entire sequence. It should be noted that the biologic activities of GXXPG-
containing peptides are not limited to elastin derivation. Laminin, for example, is
rich in LGTIPG, a sequence that displays similar bioactivity to the GXXPG
peptides derived from elastin (Mecham et al.
1989a
,
b
). Additionally, laminin
possesses other unique chemotactic sequences (Adair-Kirk et al.
2003
).
It is important to recognize that mature elastic fibers do not display chemotactic
properties. The biological properties residing within these short, 5- to 6-residue
peptides remain hidden within the hydrophobic mass of an elastic fiber. Because
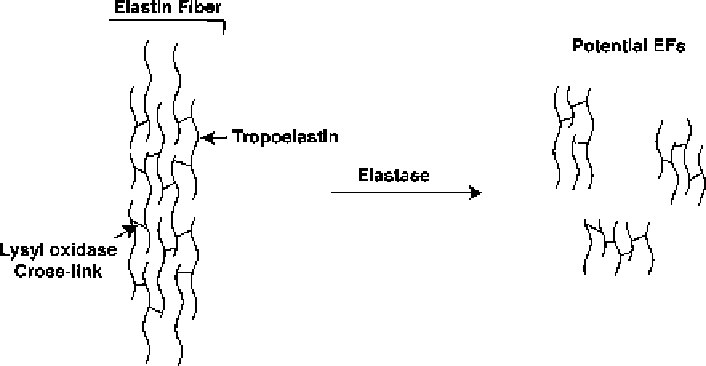
elastic fibers are extensively cross-linked, cleavage of the protein does not generate
short, linear, bioactive peptides. EFs liberated into lung lavage fluid after cigarette
smoke exposure range from ~35 to 50 kDa (Fig.
9.3
). These products are a
heterogeneous mixture of degradation products, most of which possess bioactive
sequences within them.
Fig. 9.3 Depiction of an elastic fiber. The schematic depicts an elastin fiber that consists of
multiple tropoelastin monomers cross-linked together by lysyl oxidase. Potential degradation
products and their cross-linked nature are shown (Reproduced with permission by the author
AMH.)