Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Primary CAM
Tumor
Neutrophil
Influx
Tumor
Angiogenesis
Tumor Cell
Intravasation
Control
IgG
Anti IL-8
Antibody
Tumor cells stained
for CD44 (brown)
Neutrophils stained
for chicken MMP-9
(brown)
Blood vessels
stained with SNA
(brown)
Tumor cells (green) in the
distal CAM (vasculature
stained red with LCA)
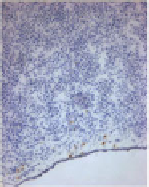
Fig. 7.6 Concomitant inhibition of neutrophil influx, tumor angiogenesis, and tumor cell intra-
vasation by anti-IL-8 treatment of primary CAM tumors. Primary CAM tumors developed from
highly disseminating variant of HT-1080 fibrosarcoma (HT-hi/diss) were treated with control IgG
(
top panels
) or function-blocking anti-IL-8 antibodies (
bottom panels
).
Left panels
: Sections of
control or anti-IL-8-treated tumors are stained for human CD44 to discriminate tumor cells
(
brown
) from chicken cells. Tumor cells are easily identified as invading CAM mesoderm,
which is highlighted by hematoxylin staining (
blue
). IL-8 treatment did not appear to affect
primary tumor growth.
Middle left panels
: Neutrophils, the major source of MMP-9 in the
CAM, are highlighted by specific staining for chicken MMP-9 (
brown
). The highest density of
neutrophils is at the tumor border, although numerous neutrophils could be identified in the tumor
interior. IL-8 treatment significantly diminished the influx of MMP-9-positive neutrophils both at
the tumor border and tumor interior.
Middle right panels
: Blood vessels (
brown
) are stained with
Sambucus
nigra
agglutinin (SNA), which binds to chicken endothelial cells. Blood vessels in the
mesoderm and the remnants of ectoderm capillary plexus are visible in compressed CAM, which is
underlined by the endoderm layer (
blue
). Angiogenic blood vessels appear to originate in the CAM
and traverse upward into the primary tumor. IL-8 significantly diminishes tumor-induced angio-
genesis.
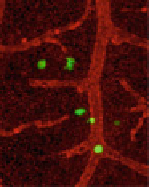
Right panels
: Intravasated GFP-tagged HT-hi/diss cells (
green
) are identified by live
immunofluorescent cell imaging in the distal CAM of tumor-bearing embryos injected with Lens
culinaris
agglutinin to highlight the vasculature (
red
). Spontaneously disseminating cells appear
either inside the vessels, at the tips of terminal capillaries, extravasating from the capillaries or
already within the CAMmesoderm. IL-8 treatment appears to significantly diminish the number of
intravasated cells at the distal portions of the CAM, which can be independently confirmed by
quantitative
Alu
PCR analysis
within 10 min (Deryugina et al.
2009
; Subauste et al.
2009
), most probably due to
size restriction. The arrest of intracardially inoculated tumor cells in liver and lung
of rats appears to occur in less than 20-30 min, but without size restriction,