Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Tumor-Associated
Neutrophil
(TAN)
rapid release
of secretory
granules
release of
proMMP-9 from
granules
rapid activation
of proMMP-9
activated
MMP-9
secretory granules
containing pre-stored
TIMP-free proMMP-9
TIMP-free proMMP-9
readily available for
activation
Tumor-Associated
Monocyte/Macrophage
(TAM)
synthesis and secretion of
proMMP-9 and TIMP-1
slow activation of proMMP-9
due to TIMP-1 hindrance
proMMP-9
complexed with
TIMP-1
activated MMP-9
still complexed with
TIMP-1
Tumor-Associated
Fibroblasts
(TAF)
?
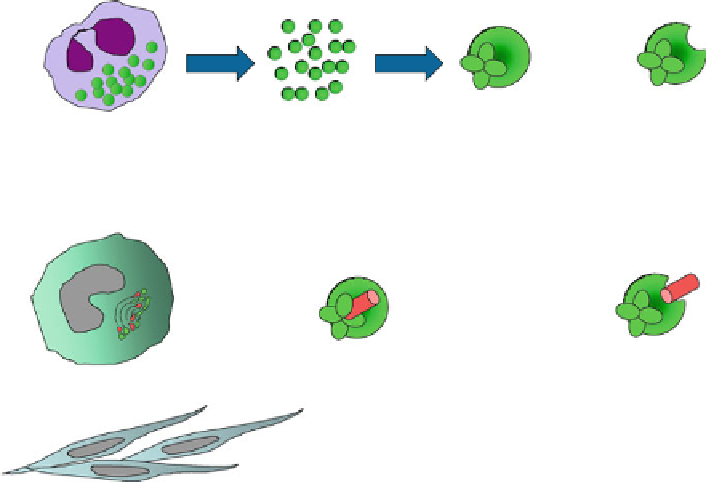
Fig. 7.4 Mechanisms involved in the activation of proMMP-9 produced by different tumor-
associated cell types. The schematic depicts secretion and subsequent activation of TIMP-free
proMMP-9 by tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) and TIMP-complexed proMMP-9 by tumor-
associated macrophages (TAMs) and fibroblasts (TAFs). Activated TANs are the only abundant
inflammatory cell type that is capable of rapid release of secretory granules containing prestored
proMMP-9. Moreover, since neutrophil MMP-9 is uniquely produced as a TIMP-free proenzyme,
it is readily available for activation. Other cells types, including tumor-associated monocytes/
macrophages (TAMs) and likely tumor-associated fibroblasts (TAFs) synthesize MMP-9 de novo
following cell activation and secrete proMMP-9 in a stoichiometric complex with TIMP-1.
Complexed TIMP-1 delays activation of proMMP-9 and can also inhibit activated MMP-9 enzyme
exceptionally potent proangiogenic MMP and that this potency of neutrophil
MMP-9 is attributed to its TIMP-free status (Fig.
7.4
). While all thus far tested
cells, including monocytes/macrophages and tumor cells, produce proMMP-9 com-
plexed with TIMP-1, which severely dampens its activation and proteolytic activity,
inflammatory neutrophils rapidly release proMMP-9 free of TIMP (Opdenakker
et al.
2001
). Therefore, in a given inflammatory environment, neutrophil MMP-9
would be immediately available for activation to rapidly execute proteolytic matrix
degradation and remodeling at the sites of angiogenesis or tumor development (Ardi
et al.
2007
,
2009
). Remodeling of the ECM by neutrophil MMP-9 is accompanied
mainly by the release of sequestered FGF-2 (Ardi et al.
2009
), while MMP-9
produced by macrophages is usually associated with mobilization of VEGF
(Bergers et al.
2000
; Giraudo et al.
2004
). Since both FGF-2 and VEGF are major
proangiogenic factors (Ferrara et al.
2003
; Presta et al.
2005
; Ellis and Hicklin
2008
;