Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
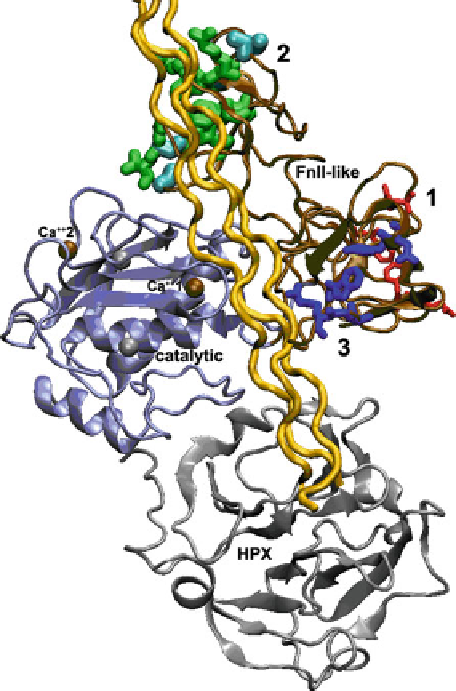
Fig. 6.4 Binding sites and proposed path of triple helix and gelatin past FnII-like modules of type
IV collagenases. The crystal structure of MMP-2 (Morgunova et al.
1999
) (PDB code 1CK7) is
plotted with catalytic domain (
ice blue
) in standard orientation and prodomain omitted. The most
extensive patch of contacts with triple helices and gelatin is indicated by
green residues
with thick
side chains in module 2 of the FnII-like insert, the second main site of contacts with
blue side
chains
of medium thickness in module 3, and ancillary contacts with
red
and thin side chains in
module I.
Cyan-colored residues
mark the site of MMP-9 mutations in its FnII-like module II that
disrupt interactions with gelatin (Collier et al.
1992
). The area corresponding to the confirmed
exosite colored
dark red
in Fig.
6.3
lies to the right of Ca
++
1 under this hypothesized path of a
collagen triple helix (
gold
). The crystal structure of a collagen triple helix (Bella et al.
1994
)(
gold
,
1CAG.pdb) has been docked by hand into the groove between the FnII-like modules (
brown
) and
the catalytic domain; the linear path shown across the HPX domain is not proposed but is simply
the complication of the linearity of triple helical coordinates available
This agrees with low
M
K
m
values of MMP-2 hydrolysis of placental type IV
m
collagen enriched in
1 chains (Monaco et al.
2007
; Gioia et al.
2009
). These
authors also measured
K
m
values as much as 100-fold weaker for placental type IV
collagen enriched in
a
2 chains. By contrast, MMP-9 has (a)
K
m
values for intact or
a