Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
S
3
S
3
α
2(I)
α
2(I)
S
1
'
S
1
'
Y191
Y191
b
S
3
S
3
Y191
Y191
S
1
S
1
S
1
'
S
1
'
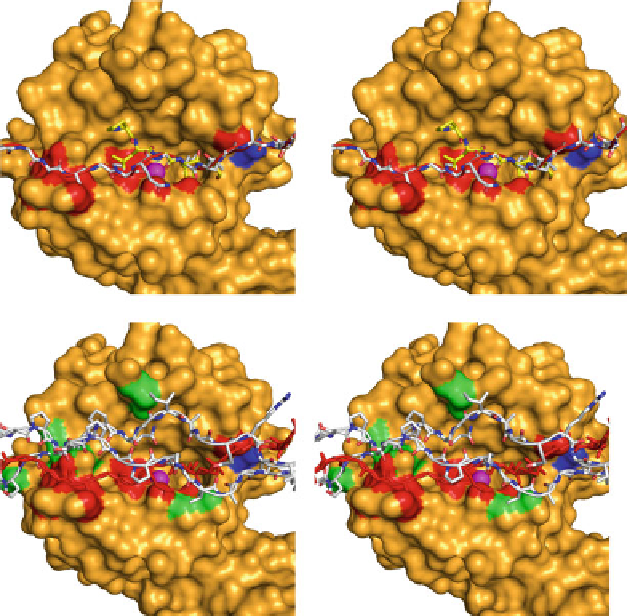
Fig. 5.3 Triple helical collagen does not fit in the active of MMP-1. (a) Stereo image of the
catalytic domain of MMP-1 was first docked with the peptide substrate PLGFA (a stick model in
yellow
) in the active site of the enzyme using Autodock. The S
3
(pro), S
2
(Leu), and S
1
0
(Phe) sites
are indicated. The
2(I) chain in the native conformation determined by Orgel et al. (
2006
) (in
stick model) containing the MMP cleavage site sequence (PGPQG~LLGAP) was then super-
imposed on the cleavable peptide bond of the PLGFA peptide. In this conformation
a
2(I) severely
clashes with the MMP-1 catalytic domain (indicated as
red
surface). This demonstrates that the
a
a
2(I) chain cannot fit into the MMP active site in the native conformation. Y191 is shown in
dark
blue
.(b) Stereo image of MMP-1 docked with the two
a
1(I) chains in addition to the
a
2(I) chain.
The colour coding is the same as in A, except that
a
2(I) chain is in
red
and additional clashes by
the
1(I) chains are shown as
green surfaces
(MMP-1 structure is 1FBL.pdb; collagen structure
courtesy of J.P.R.O. Orgel; figure made with Pymol.)
a
site, it is still in its polyproline type II-like conformation and there are several
molecular clashes elsewhere in the active site cleft. The P
4
0
(Ala) is away from the
enzyme, and there is no contact with Tyr
191
of MMP-1, which affects its collage-
nolytic activity (Chung et al.
2000
). When the two
2(I)
chain, they made a few additional clashes with MMP-1. This modelling exercise
indicates that naturally occurring unfolding of
a
1(I) chains were added to
a
2(I) at room temperature is a very
poor substrate for MMP-1 and that considerable conformational changes need to
occur for an effective hydrolysis of triple helical collagen.
a