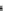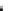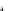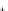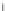Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
protein with extracellular N-terminal metalloproteinase and Hpx domains and with
a short intracellular C-terminal domain.
5.2.2 Activation of pro-MMP-1, -8 and -13
The activation of pro-MMPs is an important regulatory step for collagenolysis and
depending on the form generated, collagenolytic activity varies five- to tenfold. As
demonstrated for many secreted pro-MMPs, procollagenases are activated by a
stepwise activation mechanism (Woessner and Nagase
2000
) (see Fig.
5.1
). This
may be initiated by proteolytic attack by a number of tissue or plasma proteinases
that cleave near the middle of the propeptide, the so-called “bait” region. This
partially activates procollagenase. Final removal of the propeptide is either by
autocatalysis or by other MMPs. In the case of MMP-1 and MMP-8, the second
processing step dictates the level of enzyme activity depending on the sites of
cleavage. The bait region-cleaved MMP-1 autocleaves the Phe
81
-Val
82
or Val
82
-
Leu
83
bond (residues are numbered taking the first residue of the proenzyme as 1),
but the forms generated express only 10-20% of full collagenolytic activity (Suzuki
et al.
1990
). In the presence of pro-MMP-3, which is activated by similar pro-
teinases, the Gln
80
-Phe
81
bond is cleaved, and this form with N-terminal Phe
81
exhibits full collagenolytic activity (Suzuki et al.
1990
). The action of MMP-3 on
MMP-1 activation can be substituted by MMP-2, -7 or -10. Therefore, the avail-
ability of these MMPs in the tissue influences the local collagenolysis of the tissue.
Partial and full activation have also been described for pro-MMP-8 (Kn
auper
et al.
1993b
). After initial activation of pro-MMP-8 by proteinases, MMP-8 under-
goes autolysis and generates forms with Met
80
or Leu
81
at the N-terminus that are
€
linker
region
pro
catalytic domain
Hpx domain
Zn
2+
C
C
C
(A) MMP-1
FPATLETQEQDVDLVQKYLEKYYNLKNDGRQVEKRRNSGPVVEKLKQMQEFFGLKVTGKPDAETLKVMKQPRCGVPDVAQFVLTEGNPRWEQTHLTY
MMP-1
*
MMP-1
*
Plasmin
PKK
Trypsin PKK
MMP-10, MMP-3
MMP-7, MMP-2
(B) MMP-2
APSPIIKFPGDVAPKTDKELAVQYLNTFYGCPKESCNLFVLKDTLKKMQKFFGLPQTGDLDQNTIETMRKPRCGNPDVANYNFFPRKPKWDKNQITY
MT1-MMP
MMP-2, MMP-1, MMP-7
(C) MMP-8
FPVSSKEKNTKTVQDYLEKFYQLPSNQYQSTRKNGTNVIVEKLKEMQRFFGLNVTGKPNEETLDMMKKPRCGVPDSGGFMLTPGNPKWERTNLTY
Tissue KK
MMP-8
*
Trypsin
Trypsin
MMP-3
MMP-10
(D) MMP-13
LPLPSGGDEDDLSEEDLQFAERYLRSYYHPTNLAGILKENAASSMTERLREMQSFFGLEVTGKLDDNTLDVMKKPRCGVPDVGEYNVFPRTLKWSKMNLTY
MT1-MMP Plasmin
MMP-3
Plasmin
MMP-2, MMP-3,
MMP-13, MT1-MMP
(E) MMP-14
ALASLGSAQSSSFSPEAWLQQYGYLPPGDLRTHTQRSPQSLSAAIAAMQKFYGLQVTGKADADTMKAMRRPRCGVPDKFGAEIKANVRRKRYAIQGL
Plasmin Furin
Plasmin
Fig. 5.1 Propeptide sequence and the cleavage sites identified during activation of pro-MMPs.
See the text for details