Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
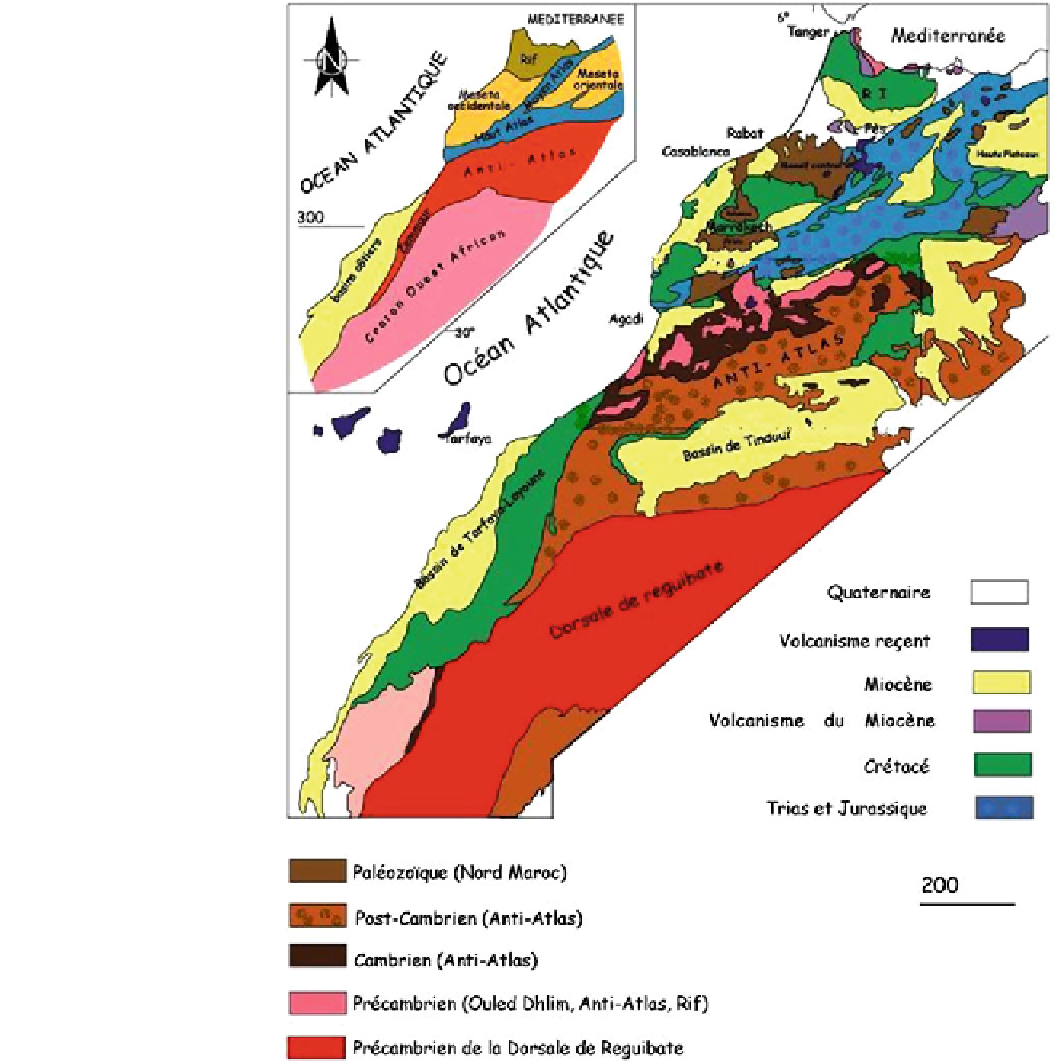
Fig. 1
Main geological domains
of Morocco
s pal-
aeontological heritage. - The Promotion of sustainable
development. - The Education of the general public and
students, by familiarizing them with the richness and
value of the palaeontological heritage.
Morocco is the world leader in the production of phos-
phate and its derivatives. The phosphate deposits are
exposed in four basins, which, from the North to the South,
are (Fig.
2
): Ouled Abdoun, with the mining town of
Khouribga; Ganntour, with the towns of Youssou
- The Protection and conservation of the country
'
importance East of the town of Essaouira; and Oued Edda-
hab in the Moroccan Sahara, with La
ä
youne as the admin-
istrative-mining town with the Port.
The Moroccan phosphate series consists of an intercrop-
ping friable, to more or less indurate, phosphate horizons with
sterile layers of a varying lithology [clays, marl, limestone and
fl
int in patches or scattered (Fig.
3
)]. One of the interesting
characteristics of Moroccan phosphate deposits is that the
layers are generally horizontal except in proximity to the Atlas
Mountains (such as in Imin Tanout, near the town of Mar-
rakech), which facilitates easy and detailed sampling (Fig.
4
).
a and
Benguerir; Meskala, a small basin without great economic