Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
where
E
y
(
z
)isthe Young's modulus of the beam as a function of its thickness
z
.With reference to
Figure 2.30b
, the moment of the force about the neutral
plane NA is given as
E
y
(
z
)
z
2
adz
R
=
±
F
.
z
(2.14)
The total bending moment on the rectangle beam is the sum of the individ-
ual moments on all the elements
dz
[76], which can be expressed as
t
/
2
a
R
E
y
(
z
)
z
2
dz
Bending Moment
=
(2.15)
−
t
/
2
This bending moment is equal to the applied moment at each point in the
beam (which depends on the applied force and its distance from the specific
point). The geometric moment of inertia
I
, which describes the effect of the
rectangular shape of the beam cross section, is given as [77]
az
2
dz
I
=
(2.16)
a
z
3
3
t
2
at
3
12
I
=
2
=
(2.17)
−
t
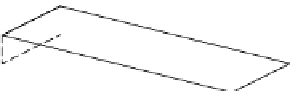
Now, consider the cantilever beam as shown in
Figure 2.31
; the beam has
a length of
L
, width of
w
, and thickness of
t
with one of the ends fixed in
cantilever form. The cantilever beam is homogeneous and symmetrical and
has a constant value of
E
y
.Aforce
F
is applied to the free end of the beam,
and the amount of deflection
y
at a distance
L
from the fixed end can then be
determined. The radius of curvature
R
is defined as [76]
d
2
y
dx
2
1
R
=
(2.18)
1
dx
2
dy
3
2
+
y
t
L
x
W
FIGURE 2.31
A cantilever beam.



















Search WWH ::

Custom Search