Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
u(x,t=0)
u(x,t=0.25)
u(x,t=0.5)
u(x,t=1)
u(x,t=3)
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
b
u(x,t=0)
u(x,t=0.25)
u(x,t=0.5)
u(x,t=1)
u(x,t=3)
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0
2
4
6
8
10
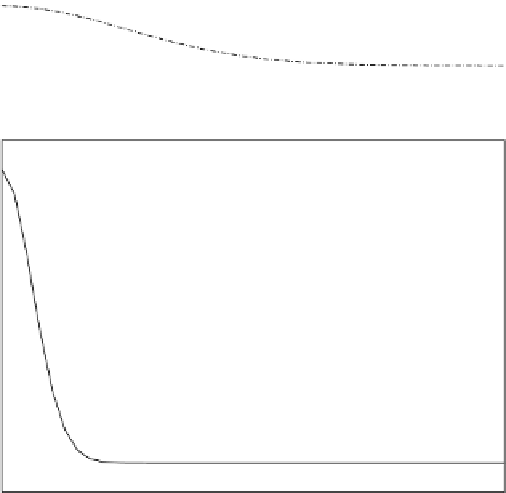
Fig. 7.3
(
a
) Concentration along the tube axis in Fig.
7.2
.(
b
) Concentration computed by a
corresponding purely one-dimensional model
three-dimensional problem in Cartesian coordinates, which in many applications
can be reduced to a one-dimensional radial problem in spherical coordinates.
Approximate Variation along a Line
Sometimes we can work with a one-dimensional model even when it cannot be
well justified mathematically or physically. Consider putting a can of beer in the
refrigerator. If we want to compute how the temperature inside the can decreases