Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
F
0
(
x
)
x
1
x
0
f
(
x
)
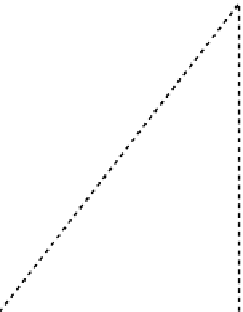
Fig. 4.4
The figure shows the function f , a linear approximation F
0
.x/, and how to compute x
1
from x
0
F
0
.x/
D
f
0
.x
0
/;
so, in particular,
F
0
.x
0
/
D
f
0
.x
0
/:
Hence, both the value and the derivative of f and F
0
coincide at the point x
D
x
0
.
If we now define x
1
to be such that
F
0
.x
1
/
D
0;
(4.57)
we get
f.x
0
/
C
.x
1
x
0
/f
0
.x
0
/
D
0;
(4.58)
and thus
f.x
0
/
f
0
.x
0
/
;
x
1
D
x
0
(4.59)
which is identical to (
4.52
). Again, we can repeat this process by defining a linear
approximation of f around x
1
,
F
1
.x/
D
f.x
1
/
C
.x
x
1
/f
0
.x
1
/:
(4.60)
By defining x
2
to be such that
F
1
.x
2
/
D
0;
(4.61)