Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Ante-mortem inspection
The purpose of ante-mortem inspection is to ensure that
only clean, healthy residue and stress-free animals are
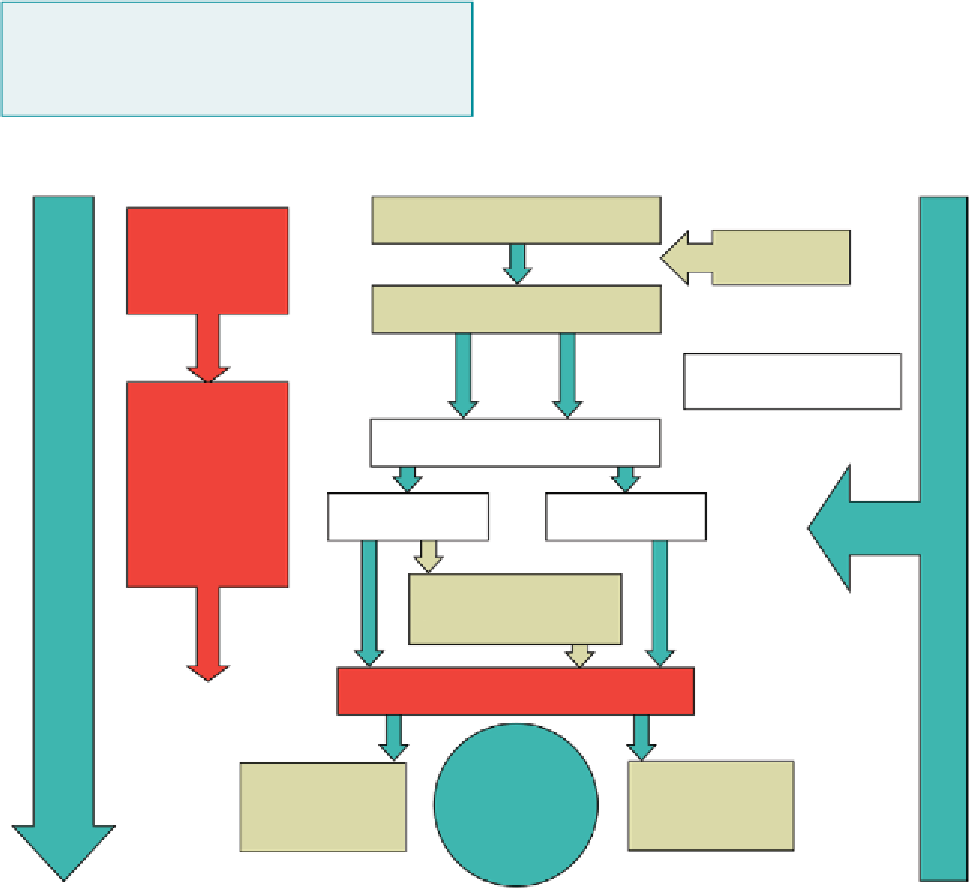
presented for slaughter. As illustrated in Figure 9.2, the
effective preselection of animals on farm into high and
low risk is key to an 'Integrated Food Safety Assurance.
To allow farms to be categorised into groups with animals
presenting equivalent risk to public health, EFSA has
suggested the use of harmonised epidemiological indicators
(HEIs) for potential hazards (EFSA, 2011, 2012).
As examples, the EFSA opinions propose HEIs for
Trichinella
,
T. gondii
,
Salmonella
and
Y. enterocolitica
in pigs;
Salmonella
,
Campylobacter
and extended-spectrum/AmpC
β-lactamase producing
E. coli
in poultry; and
Salmonella
and verotoxigenic
E. coli
in cattle. The application of
these requires actions on farm, for example, controlled
housing for pigs or 'clean hide' interventions for cattle. The
standards for these interventions must be harmonised if the
HEIs are to have any meaning.
The concept is applicable to the consideration of risk
from 'farm to fork' and could be used to standardise risk
not just between production units but also between
slaughter establishments.
As discussed, the inspection of individual animals, or
groups of animals in the slaughterhouse lairage without
reliable information from the farm, akin to a veterinary
examination without a history, is limited. Selection of
animals into groups of greater or lesser risk based, at this
point, on incomplete data, for example, on age alone,
is impossible to justify.
Consequently, any suggestion that a less rigorous
online post-mortem inspection regimes should be intro-
duced before a reliable system of food chain information
on which public health risk can be assessed is in place
would be foolhardy.
An epidemiological indicator is defined as the prevalence or
incidence of the hazard at a certain stage of the food chain
or an indirect measure of the hazard that correlates to human
health risk caused by the hazard.
Parent/Breeding stock
Herd/flock
health farm
audits
Feed safety
Production stock
Food Chain Information
Livestock Risk Categorisation
High Risk
Low Risk
Food saftey
management
system
incorporating
HACCP
principles
Ante-mortem Inspection
High Risk Lines
Lower Risk Lines
Improvement in technology/
carcase decontamination
Hygiene target
Food
Safety
Objective
Diverted for pathogen
reducing or
processing
Can be used for fresh
chilled products
Figure 9.2
Integrated food safety assurance.