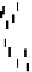Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
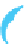
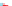
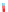
Decreasing surface tension Wetting, spreading and angle of contact
The effect varies depending on the nature of the surfactant
α
~360°
No wetting, no
gravity influence
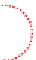
No wetting,
gravity influence
Partial wetting
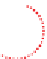
α
~0°
Improved wetting
Complete wetting
Figure 5.1
Showing progressive wetting of a solid surface (Reproduced with permission from Ecolab. © Ecolab).
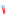
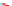
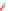
Detergent solution
Oil
Hard surface
Figure 5.2
Wetting, roll-up and formation of emulsion (Reproduced with permission from Ecolab. © Ecolab).
Emulsification
Emulsions are suspensions of small
droplets of one fluid in another. Milk, for example, is an
emulsion of milk fats and proteins in water, stabilised by
other molecules and ions present in the milk. Fats, oils
and greases will not naturally disperse in water. First, the
oil needs to be released from the surface it is resting on.
Wetting is the first stage in this as the detergent under-
mines the oil-surface attraction and starts to displace the
oil, which starts to roll up into droplets. This is acceler-
ated if the temperature is high enough to soften or fully
liquefy the oil or grease and/or if mechanical energy is
applied to the soil. The oil droplets break away from the
surface and float freely. Unless prevented from doing so,
these droplets would coalesce as they contacted each
other at random and would eventually become large
enough to re-deposit elsewhere. To prevent the coales-
cence, surfactants, either those involved in the wetting or
other specialist emulsifiers, coat the surface of the oil
droplets and stabilise the emulsion (Fig. 5.2).
Dispersion
This is similar to emulsification except
that it involves the breaking up and suspension of solid
particles rather than fluid droplets. Dispersion is often
carried out in a detergent by components other than sur-
factants, usually inorganic materials such as carbonates,
silicates or phosphates or, in more advanced formula-
tions, by special water-soluble charged polymers. The
mechanism of maintaining a stable dispersion, thus