Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Golgi apparatus
cytoplasm
rough ER
chromatin
mitochondrion
ribosomes
nucleolus
smooth ER
nucleoplasm
nuclear membrane
nucleus
lysosome
vacuole
plasma membrane
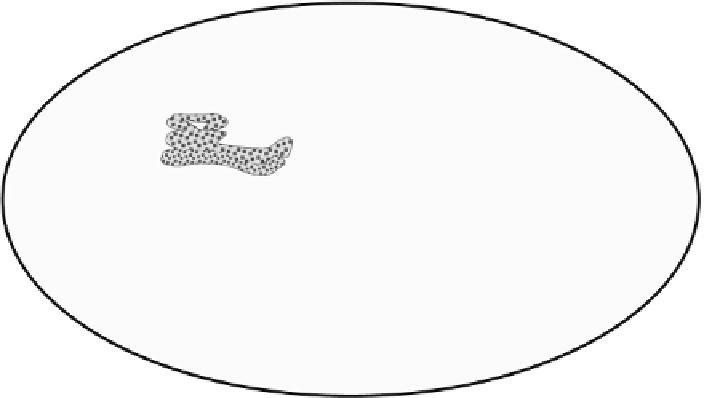
Fig. 1.1
Schematic diagram of a cell, showing different constituent parts. (Components illustrated
here do not represent the true structure observed in a biological cell.) The constituents shown here
are found in an animal cell. In a plant cell, in addition to all these structures, chloroplasts involved in
photosynthesis also exist. A plant cell (not an animal cell) also consists of a cell wall surrounding the
plasma membrane which provides tensile strength and protection against mechanical and osmotic
stress
within the nucleus that is protected by the nuclear envelope. The rest is contained
in mitochondria. Within the nucleus is the nucleolus which functions as the site of
ribosomal-RNA synthesis. The diameter of a nucleus ranges between 3 and 10
µ
m.
Despite many differences, both animal and plant cells have striking similarities in
their organization and functions.
Although the origins of most of the cellular processes are not yet discovered,
organisms that are made up of cells have been classified depending on the structure
and organization of cellular building blocks. Organisms that exist as single cells are
called unicellular—
Archaea
and
Bacteria
. Organisms that are made up of groups
of cells working together are called multicellular—animals, fungi and plants. There
is another kingdom which contains a mixture of both unicellular and multicellular
organisms. This is called the
Protista
. Humans have about 10
14
cells in their bodies;
a typical cell size in the human body is of the order of 10
m, with a mass of 1 ng.
A schematic diagram showing different parts in a cell is presented in Fig.
1.1
.
All cells are enclosed by cell envelopes which consist of cell walls covering plasma
membranes. This topic is dedicated to a better understanding of various aspects of
cellular membranes. A more detailed explanation of the structure and functions of
the cell's various components can be found in many text books on cell biology. In this
topic, we mainly focus on those cell components whose structure and functions are
connected with the processes taking place inside membranes.
µ


























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search