Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
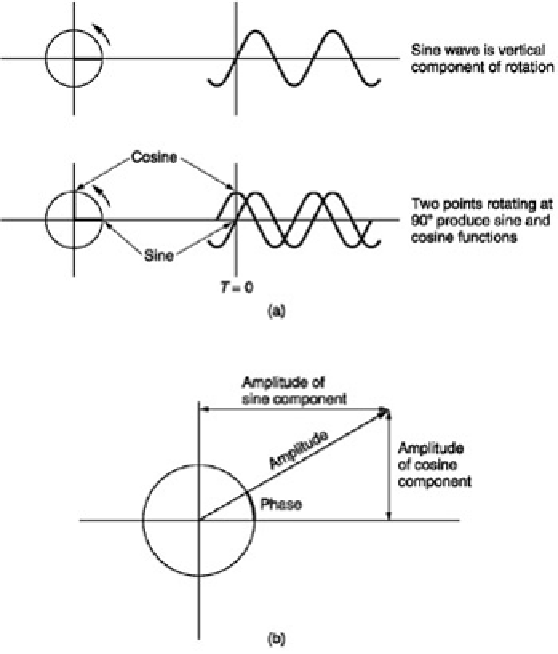
Figure 3.38:
The origin of sine and cosine waves is to take a particular viewpoint of a rotation. Any phase can be
synthesized by adding proportions of sine and cosine waves.
Figure 3.38
shows that the proportions necessary are respectively the sine and the cosine of the phase angle.
Thus the two methods of describing phase can be readily interchanged.
The discrete Fourier transform spectrum-analyses a string of samples by searching separately for each discrete
target frequency. It does this by multiplying the input waveform by a sine wave, known as the basis function, having
the target frequency and adding up or integrating the products.
Figure 3.39
(
a) shows that multiplying by basis
functions gives a non-zero integral when the input frequency is the same, whereas
Figure 3.39
(b) shows that with a
different input frequency (in fact all other different frequencies) the integral is zero showing that no component of
the target frequency exists. Thus from a real waveform containing many frequencies all frequencies except the
target frequency are excluded. The magnitude of the integral is proportional to the amplitude of the target
component.