Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 2.21:
(a) In MPEG-1, colour difference information is downsampled and shifted so that it is symmetrically
disposed about the luminance pixels. (b) In MPEG-2 the horizontal shift was abandoned.
The sampling rates of ITU-601 are based on commonality between 525- and 625-line systems. However, the
consequence is that the pixel spacing is different in the horizontal and vertical axes. This is incompatible with
computer graphics in which so-called 'square' pixels are used. This means that the horizontal and vertical spacing
is the same, giving the same resolution in both axes. However, high-definition TV and computer graphics formats
universally use 'square' pixels. MPEG can handle various pixel aspect ratios and allows a control code to be
embedded in the sequence header to help the decoder.
2.10 The phase-locked loop
All digital video systems need to be clocked at the appropriate rate in order to function properly. Whilst a clock may
be obtained from a fixed frequency oscillator such as a crystal, many operations in video require
genlocking
or
synchronizing the clock to an external source.
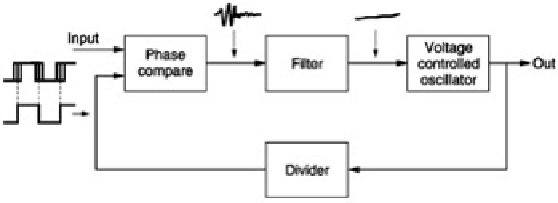
In phase-locked loops, the oscillator can run at a range of frequencies according to the voltage applied to a control
terminal. This is called a voltage-controlled oscillator or VCO.
Figure 2.22
shows that the VCO is driven by a phase
error measured between the output and some reference. The error changes the control voltage in such a way that
the error is reduced, so that the output eventually has the same frequency as the reference. A low-pass filter is
fitted in the control voltage path to prevent the loop becoming unstable. If a divider is placed between the VCO and
the phase comparator, as in the figure, the VCO frequency can be made to be a multiple of the reference. This also
has the effect of making the loop more heavily damped, so that it is less likely to change frequency if the input is
irregular.
Figure 2.22:
A phase-locked loop requires these components as a minimum. The filter in the control voltage serves
to reduce clock jitter.
In digital video, the frequency multiplication of a phase-locked loop is extremely useful.
Figure 2.23
shows how the
13.5 MHz clock of component digital video and the 27 MHz master clock of MPEG are obtained from the sync
pulses of an analog reference by such a multiplication process.