Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Consequently, 1 mW in 600 requires 0.775 V. With a sinusoidal alternating input (b), the power is a sine square
function which can be averaged over one cycle. A DC voltage which would deliver the same power has a value
which is the square root of the mean of the square of the sinusoidal input.
The deciBel is a logarithmic measuring system and has its origins in telephony
[
2
]
where the loss in a cable is a
logarithmic function of the length. Human hearing also has a logarithmic response with respect to sound pressure
level (SPL). In order to relate to the subjective response audio signal level measurements have also to be
logarithmic and so the deciBel was adopted for audio.
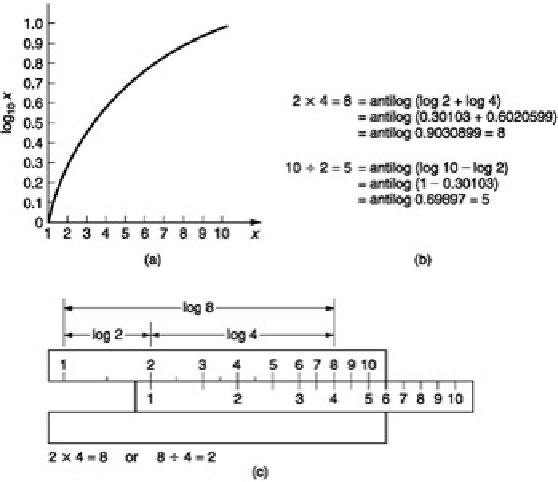
Figure 4.2
shows the principle of the logarithm. To give an example, if it is clear that 10
2
is 100 and 10
3
is 1000,
then there must be a power between 2 and 3 to which 10 can be raised to give any value between 100 and 1000.
That power is the logarithm to base 10 of the value. e.g. log
10
300 = 2.5 approx. Note that 10
0
is 1.
Figure 4.2:
(a) The logarithm of a number is the power to which the base (in this case 10) must be raised to obtain
the number. (b) Multiplication is obtained by adding logs, division by subtracting. (c) The slide rule has two
logarithmic scales whose length can easily be added or subtracted.
Logarithms were developed by mathematicians before the availability of calculators or computers to ease
calculations such as multiplication, squaring, division and extracting roots. The advantage is that armed with a set
of log tables, multiplication can be performed by adding, division by subtracting.
Figure 4.2
shows some examples.
It will be clear that squaring a number is performed by adding two identical logs and the same result will be
obtained by multiplying the log by 2.
The slide rule is an early calculator which consists of two logarithmically engraved scales in which the length along
the scale is proportional to the log of the engraved number. By sliding the moving scale two lengths can easily be
added or subtracted and as a result multiplication and division are readily obtained.
The logarithmic unit of measurement in telephones was called the Bel after Alexander Graham Bell, the inventor.
Figure 4.3
(a) shows that the Bel was defined as the log of the
power
ratio between the power to be measured and
some reference power. Clearly the reference power must have a level of 0 Bels since log
10
1 is 0.