Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Infectious
progeny
virus
Virus
infection
(
α, β
)
Mitogenic
antigenic
stimulation (
γ
)
IRP IFN-regulated
proteins
IRF3
IRF7
IL12
IL18
γ
α
β
γ
γ
α β
IFN
IFN
α β
IFN genes
Ch 9
α
n
,
β
Ch 12
Jak-STAT
IRF
Interferon
β
,
α
4
α
2,5,6,8
Receptors
γ
Ch 6+21
γ
α β
Ch 21
Interferon-treated
cell
IFN action
Infected (stimulated)
cell
IFN production
Figure 1.15
Illustration of IFN signaling mechanism.
challenge from a continuum of hostile behaviors and needs to respond judiciously
through a coordinated decision process (Tew et al., 1997).
h e protein interferon (IFN) is produced by cells when they are invaded by
viruses; it is released into the bloodstream or intercellular fl uid to induce healthy
cells to manufacture an enzyme that counters the infection. Figure 1.15 illustrates
the release of IFN by infected cells during virus infection. Since the receptor for
IFN has a common structure among diff erent host cells, the IFN that is produced
by a virus-infected cell can bind to a receptor of the neighboring cell and enters it.
IFN induces the production of IFN-regulated proteins within the neighboring cell;
such proteins inhibit the virus replication inside the cell.
h e following is a list of reasons why signaling is important in biological defense:
It allows a cell to move a signal from outside to inside.
Signaling results in changes to the cell, allowing it to appropriately respond
to a stimulus.
It allows signaling and message passing among various functional components.
It allows response to external stimuli such as cytokines, growth factors, hor-
mones, tissue repair or remodeling, and stress.
Tissue-specifi c regulation is the hallmark of virus-driven cytotoxic T cells
expansion in immune response.
Signaling regulates diff erentiation and development, and immune response.
Additionally, cells communicate with surroundings through their surface receptors
that recognize extracellular signal and convert into intracellular signal, which then






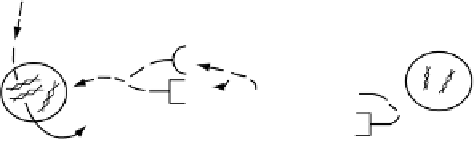



Search WWH ::

Custom Search