Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Thoracic duct
3
×
10
11
/day
Pre-T cell
Thymus
T cell
Vein
Tissues
Spleen
Lymph node
Afferent lymphatic
Postcapillary venule
Capillary
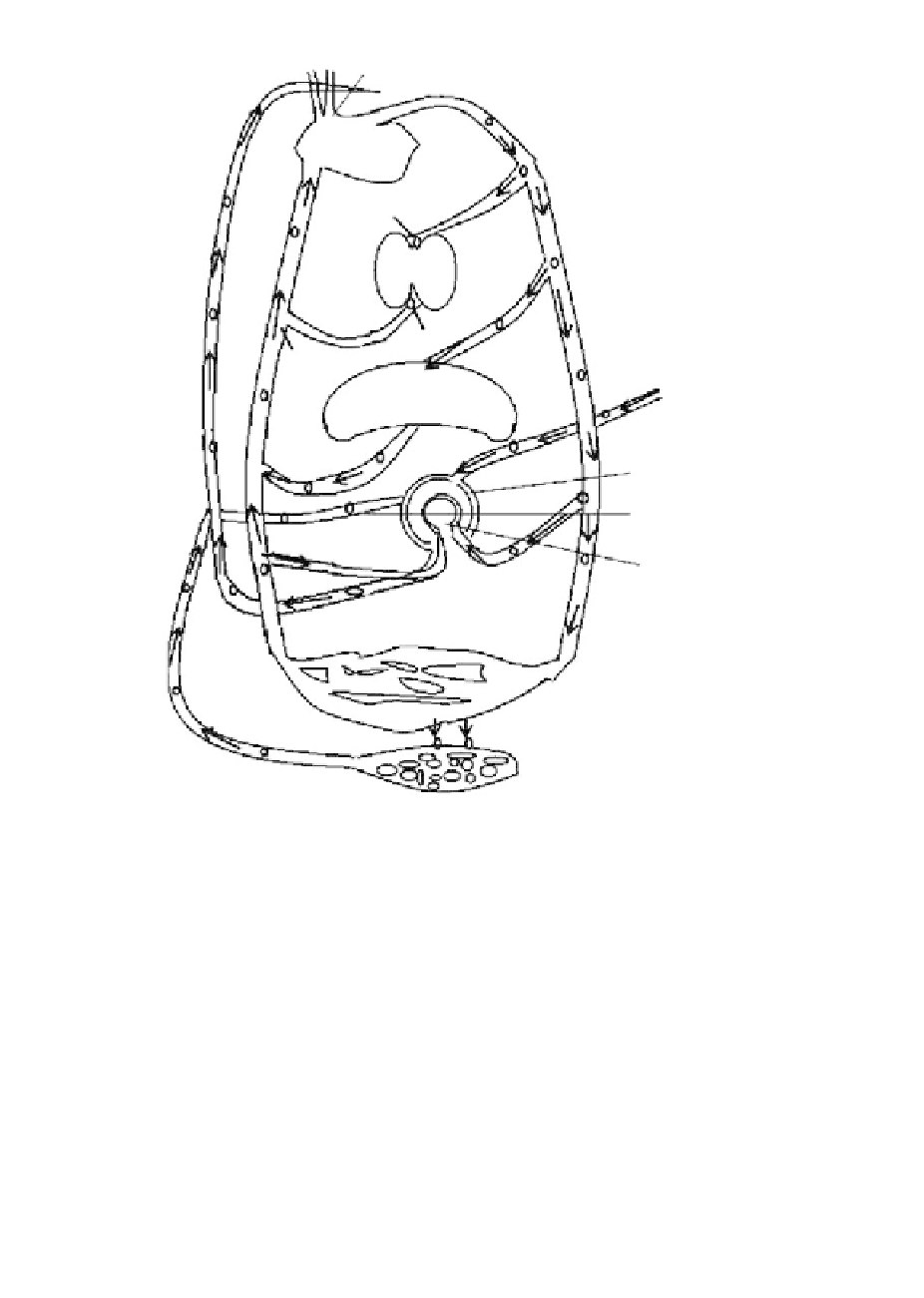
Figure 1.13 Circulation of immune cells through the blood (white) and lymph
vasculature (black) to major organs of lymphatic systems. (From Kuby, J. et al.,
Immunology,
3rd edition. W. H. Freeman, New York, 2000.)
1.4 Circulatory Mechanism
As seen earlier, the immune system is an inherently distributed system that consists
of a variety of specialized cells, enzymes, and other serum proteins, which are spread
throughout the body. Immune cells, particularly, lymphocytes circulate constantly
through the blood, lymph, lymphoid organs, and tissue spaces (Figure 1.13). h ey
visit primary and secondary lymphoid organs to interact with foreign antigens. Stud-
ies show that lymphocytes circulate through blood for 2-12 hours before appearing
in a particular lymphoid organ (Kuby et al., 2000).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search