Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
0 0 1 1
0
1
1
0
Antibody
k
k + l
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
Antibody
Figure 5.5
p
j
(
l
) is the
l
th element of string
p
representing antibody
j
(paratope
j
);
k
) is the
l
th element of the
k
th shift of the bit string
e
representing antibody
i
(epitope
i
);
d
e
i
(
l
+
=
8.
where
p
j
(
l
) denotes the
l
th element of the string
p
representing antibody
j
(paratope
j
);
e
i
(
l
+
k
) denotes the
l
th element of the
k
th shift of the bit string
e
representing anti-
body
i
(epitope
i
) (see Figure 5.5)
.
h e Exclusive OR (XOR) operator is denoted by
∧
; in fact, the
∧
operator is used to compute the Hamming distance between two
binary strings;
d
is the minimum distance between the lengths of the two bit strings
e
and
p
; also,
r
=
−
>
>
0, and
0 otherwise. Note that the a
nity defi ned in Equation 5.8 is not symmetric.
h is model (Farmer et al., 1986) defi nes a set of diff erential equations for
predicting the concentration of antibodies, based on the interaction between them
and with foreign antigens. Let
N
be the number of diff erent antibody types present
in the IN; similarly, let
n
be the number of antigen types. h en the change in the
concentration of antibodies of type
i
denoted by
x
i
is defi ned as
d
s
. A threshold function is defi ned by
G
,
G
(
x
)
0 if
x
N
N
n
dx
dt
∑
∑
∑
i
…
c
m xx
k
m xx
m xy
k
x
i
,
for
i
1,
,
N
(5.9)
ji
i
j
1
ij
i
j
ji
i
j
2
j
1
j
1
j
1
h e fi rst two terms model the interaction among antibodies; particularly, the fi rst
term represents the stimulation of the paratope of a type
i
antibody by the epitope
of a type
j
antibody, whereas the second term represents the suppression of a type
i
antibody when its epitope is recognized by the paratope of a type
j
antibody.
In the third term,
y
j
represents the concentration of antigen of type
j
. h e last
term models the tendency of cells to die when no interaction with other antibodies
occurs, and
k
2
is the cell death rate.
An important aspect of this model is that the number of antigen and antibody
types is considered dynamic. To update the total number of antigen and antibody
types, a threshold on all their concentrations is defi ned. h us the interaction of
an antibody with all other antibodies and antigens is eliminated when the con-
centration drops below such threshold. h e generation of new antibodies is done
by applying genetic operators to the paratope and epitope strings using crossover,
inversion, and point mutation. h is process is closer to a model of genetic changes
that occur during cloning than to the one that occurs when new types of antibodies
are produced in the bone marrow.




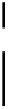

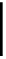







Search WWH ::

Custom Search