Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
4.6.4.1 Testing Process
h e detection process is straightforward—the generated detectors are matched with
new samples in test datasets. If a sample pattern,
x
is activated by (i.e., lies inside the
recognition hypersphere of ) a detector
y
=
(
c, r
), then an estimated distance from
x
to the self-set is computed as
µ
(
x, y
)
r
-
dist
(
x, c
), where
dist
(
x
,
c
) is the distance
between sample pattern
x
and the center of detector
y
. h en, the degree of abnor-
mality
A(x)
of a matched pattern
x
is computed as the minimum of
µ
(x, y)
among
all activated detectors,
y
, that is,
=
A
(
x
)
=
min{
µ
(
x, y
)|
y
is activated by
x
}
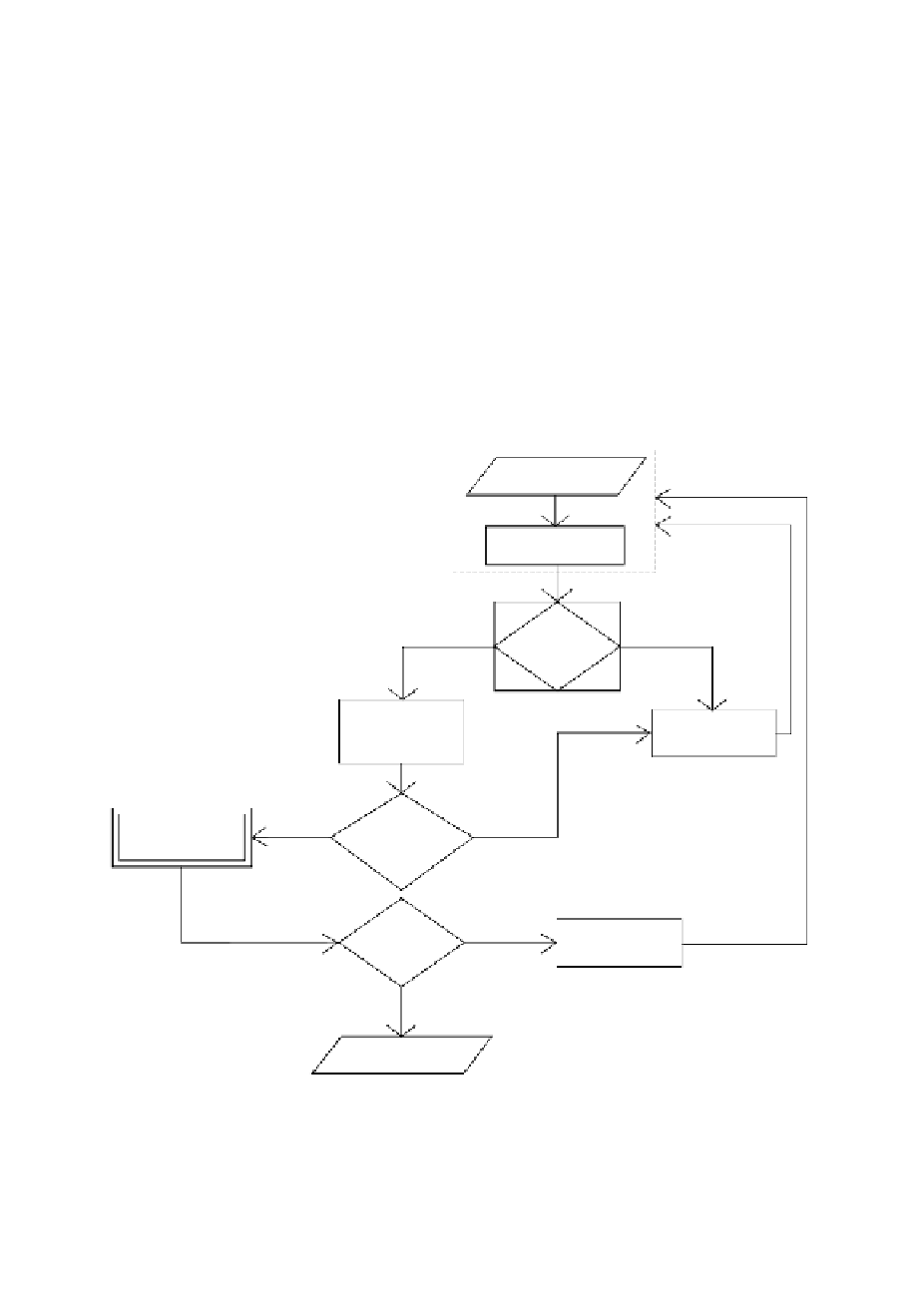
Figure 4.14 shows the fl ow diagram of the iterative approach of generating variable-
sized negative detectors.
Randomly generated
detectors
For each
candidate detector
Is
covering
self?
No
Yes
Evaluate
quality of
detector
Move the
detector
Is
overlapping
detectors?
No
Store
Yes
Set of mature
detectors (R)
Update
Is
time to
terminate?
No
Clone better
detectors (R
m
)
Yes
Exit
Figure 4.14
Flow diagram shows the steps of the variable-sized detector
generation.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search