Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Gonzalez et al. (2003b) assumed that the self-set
ˆ
consisted of a collection of
neighborhoods around each one of the self-sample points,
S
; each neighborhood
is defi ned as a hypersphere of radius
r
s
around a sample point. h erefore, the set
Ŝ
may be defi ned as
′
ˆ
:
=
∈
′
-
≤
{
x
U
: there exists
s
in
S
, ||
s
x
||
r
self
}
and the volume of
S
ˆ
is described as
∫
V
:
χ
()
x dx
S
S
U
where
∈
1
if
xS
S
:
0
if
xS
Monte Carlo methods are well-established techniques with a strong mathematical
foundation used for volume estimation, and they are being used here to estimate
the coverage of a set of detectors. Also, this technique is useful in probabilistically
estimating the overlap among detectors with diff erent shapes, which otherwise will
be cumbersome if a geometrical approach is followed.
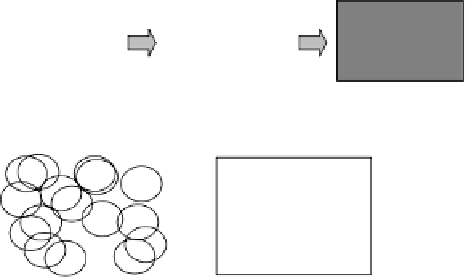
Figure 4.11 illustrates the generation of hyperspherical detectors using Monte
Carlo integration and simulated annealing.
Self-data
Generate random
population of
detectors
Optimize detector
Figure 4.11
A heuristic algorithm to generate hyperspherical negative detectors.


















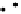



















Search WWH ::

Custom Search