Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
14
air, test 1
air, test 2
saline, test 1
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
transmural pressures (Pa)
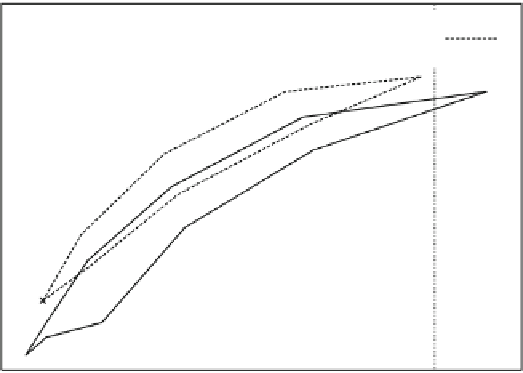
Fig. 13.1
Relationships between volume (ml per g of tissue) and pressure (Pa) in air-filled and
saline-filled lungs (Source: [
1595
]). In the case of air-filled lung, the effect of loading history is
demonstrated with the upper shift of the loop during the second cyclic loading with respect to the
first. When the lung is filled with saline, only the first cyclic loading is displayed, owing to a quasi-
superimposition of the loops of the following successive cyclic loadings with the first. The loop is
displaced leftward and upward with respect to curves in air-filled lung.
liquid and another medium, the greater the stability of the interface, and the lower
the energy involved in the formation of the interface.
Surface tension is the manifestation of intermolecular forces in the interface,
the surface shrinking to the smallest possible area. The surface tension is the force
of attraction between adjacent molecules of a liquid. Therefore, this molecular
cohesive force in the surface film tends to contract the surface.
The pressure-volume curves obtained in air-filled lungs and after filling lungs
with saline show that: (1) surface tension forces are greater during inflation than
deflation and (2) a large portion of transpulmonary pressure can be attributed to
surface tension (Fig.
13.1
).
2
The superficial tension changes with the radius of curvature of the alveolar
surface. The
Laplace law
states that the transmural pressure increases as the
2
Lung elasticity can be assessed by administration of saline solution in isolated lungs that removes
the contribution of the superficial tension. For a given lung volume, a greater pressure is required
to inflate the lung filled with air than lung filled with a saline solution. Pressure-volume loops
of liquid-filled lungs are displaced leftward and upward (low transpulmonary pressure and high
compliance) and display less hysteresis. Lung inflation with air measures both tissue and surface
tension components. Furthermore, there is a much smaller difference between the air- and liquid-
filled curves on deflation than on inflation.
















































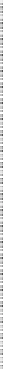
















































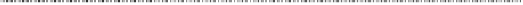


Search WWH ::

Custom Search