Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
ATP
ADP
AMP
adenosine
inosine
mucus
Aqp
CaCC
CBEx
ELF
NHEx
ENaC
CFTR
ORCC
CNT
cilium
P2Y
A2b
PIP2
CFTR
HK−ATPase
basal body
−
cAMP
IP3
Cl
Na
Cl
PKA
PKG
Ca
PKA
CFTR
endosome
H−ATPase
airway epithelial cell
H2O, Cl, Na, K
Fig. 12.1
Ion transport across the apical plasma membrane of airway epithelial cells
(Source: [
1514
]). The liquid layer at the luminal surface (airway surface liquid) of the respiratory
epithelium has 2 strata: epithelial lining fluid (ELF) and mucus layer. The respiratory cilium beats
in epithelial lining fluid, but its tip contact overlying mucus. Aquaporins and ion channels that
regulate water and ion transport are involved in production and maintenance of epithelial lining
fluid as well as mucus homeostasis. Chloride ions exit through cystic fibrosis transmembrane
conductance regulator (CFTR) are stimulated by adenosine binding to its receptor A
2B
or calcium
ions that excite Ca
2
+
-activated Cl
−
channels (CaCC) after Ca
2
+
influx upon stimulation of
nucleotide receptor P2Y
2
by ATP messenger. Channel CFTR also transports transport ATP,
sodium, bicarbonate ions, and water. Channel CFTR is activated by protein kinase-A (PKA),
cAMP, and ATP binding. In addition, CFTR is phosphorylated by protein kinases PKG1a and
PKG2. Sodium ions are imported through epithelial Na
+
channel (ENaC). Chloride channel CFTR
inhibits ENaC channel. It also regulates Cl
−
-HCO
3
exchanger (CBEx) and outwardly rectifying
Cl
−
channels (ORCC). Airway surface liquid pH is regulated by H
+
-K
+
AT P a s e a n d C l
−
-HCO
3
exchanger. Channel CFTR can activate aquaporin (Aqp). It also targets regulator NHERF of Na
+
-
H
+
exchanger NHE3 (NHEx). Channel CFTR located in membrane of endosomal vesicles can
counterbalance the activity of H
+
ATPase. Adenosine and inosine are removed from airway surface
by concentrative nucleoside transporters (CNT).
(Cl
−
and HCO
3
) secretion. On the other hand, the passive paracellular ion transfer
depends on adhesion plaques between apposed epithelial cells that confer the
permeability and ion selectivity of the paracellular path. In polarized respiratory
epithelia, the paracellular pathway is limited by tight junctions and scattered
adherens junctions. The latter localize in the lateral intercellular spaces, where
adjacent epithelial cells interdigitate. Circumferential tight junctions form the func-
tional and structural border that separates apical and basolateral compartments. Like
many other epithelia, respiratory epithelia produce multiple claudins, the primary
determinants of paracellular ion conductance.
2
Rapid regulation of transcellular
2
Different cell types of the respiratory epithelium synthesize the same claudin types that form
homo- and hetero-oligomers, both on a given cell and with those of its neighbors. Aldosterone
increases claudin-4 phosphorylation and paracellular Cl
−
permeability.











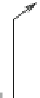





































Search WWH ::

Custom Search