Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
HSC
IL3
lymphoid SC
IL3
IL7
pre−proB lymphocyte
LGL
CD4+CD8+ TCR
proB lymphocyte
large preB lymphocyte
CD4+CD8+ TCR
αβ
small preB lymphocyte
immature B lymphocyte
mature B lymphocyte
NK lymphocyte
CD4−CD8−TCR
αβ
CD4+CD8− TH lymphocyte
CD4−CD8+ Tsuppressor
TCR αβ
antibody producing
IgM secreting
B lymphocyte
plasmacyte
memory B lymphocyte
Fig. 2.6
Formation of lymphocytes. Interleukins act on lymphocyte production. T lymphocytes
include: CD4
+
,CD8
−
helper (T
H
) T lymphocytes; CD4
−
,CD8
+
cytotoxic T lymphocytes;
CD4
−
,CD8
−
αγ
T lymphocytes; and natural killer (NK) lymphocytes. Plasmalemmal T-cell
receptor (TCR)
αβ
and
γδ
chains characterize lymphocyte subpopulations [
91
]. Normal CD4
+
,
CD8
. Lymphocytes that express CD8 can be
subdivided into distinct classes according to TCR chain expression pattern. CD4
−
lymphocytes have more than 99% of TCR
αβ
−
,CD8
+
lymphocytes express predominantly (99%) TCR
αβ
receptors. CD4
−
,CD8
−
lymphocytes have
the highest proportion (62%) of TCR
γδ
receptors.
2.4.2.8
Other Cytokines
Tumor-necrosis factor-
stimulates granulopoiesis and inhibits erythropoiesis.
Interleukins
are also involved in hematopoeisis (Fig.
2.6
).
Interleukin-1 increases the production of colony stimulating factors and stem
cell growth factor. Expression of IL2 is induced by IL1 agent. Interleukin-3 acts on
hematopoietic progenitors, in combination with other cytokines. It induces prolif-
eration of several lineages and enhances the effects of gmCSF factor. Interleukin-4
is a T-cell growth factor and promotes the differentiation of T
H0
precursors toward
the T
H2
lineage. Interleukin-5 influences eosinophil and basophil production and
functioning. It enhances IL2-dependent differentiation and proliferation of T cells.
Interleukin-6 promotes development and functioning of lymphocytes and meg-
akaryocyte maturation. Interleukin-7 acts on the lymphocyte production, as it
stimulates stem cells to form lymphoid progenitors (Fig.
2.6
). Interleukin-8 is a
chemoattractant for fibroblasts, neutrophils, basophils, T lymphocytes, and endothe-
lial cells. It also activates integrins in monocytes and eosinophils for extravasation.
Interleukin-9 acts on erythroid progenitors. Interleukin-10 inhibits the synthesis of
α





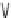




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search