Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
L−Arg
WSS
wall stretch
hypoxemia
Cam
Ca
L−Arg
Ca
substance P
Ach
Bdk
His
Ins
Cam
+
Ca
Ca
+
+
PLC
R
+
cytokines
iNOS
cNOS
5HT
ATP
IP3
+
VEGF
RGS4
−
NO
L−Cit
Ca
−
VEGFR
EC
ppET
pET
ET
NO
+
GCase
ET
GTP
cGMP
DAG
PIP2
ETR
Ca
+
IP3
C
a
Ca
−
Cl
K
SMC
Fig. 9.9
Nitric oxide and endothelin-1 synthesis, function, and regulation (Sources: [
761
,
1106
]).
Nitric oxide, discovered in endothelial cells, is produced by NO synthase from
L
arginine. It binds
to its guanylate cyclase receptors and increases the intracellular concentration of cyclic guanosine
monophosphate (cGMP). Messenger cGMP stimulates the cGMP-dependent protein kinase-G
(PKG) that precludes intracellular calcium release by impeding the activity of phospholipase-C
and inositol trisphosphate.
Nitric Oxide Synthase
Nitric oxide synthase catalyzes the conversion of
L
arginine to NO and
L
citrulline
(Fig
9.9
). Two NOS categories exist: constitutive (cNOS) and inducible (iNOS).
Ca
2
+
-calmodulin-dependent NOS resides in endothelial cells (endothelial constitu-
tive NOS [NOS3 or eNOS]) and smooth myocytes. Isoform NOS3 yields a basal
release. Enzyme NOS2 is expressed in endothelial cells in the presence of cytokines
(cytokine-inducible NOS).






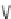

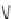








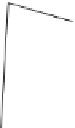

















































Search WWH ::

Custom Search