Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
integrin
VCAM1
WSS
VEGFR2
integrin
PDGFR
VE cadherin
VEGFR2
ICAM1
E−selectin
EGFR
GPCR
Cl
Na Ca MSKC
RTK
PECAM1
NOx
c−Src
catenin
K
eNOS
Sos
PLC
Shc
talin
FAK
O2
Grb2
Pax
Vinc
tensin
actinin
DAG
+
TGF
O2−
β
Src
Ras
PI3K
NO
PI3K
NF
κ
B
PKC
Rho
Rac
PKB
PDGF
ONOO−
cytoskeleton
Raf
Cdc42
H2O2
NO
cytoskeleton
MAP2K
−
JNK
proMMP
ERK
−
TnxIP
MMP
p38
−
TGF
α
Tnx
transcription
−
+
ASK1
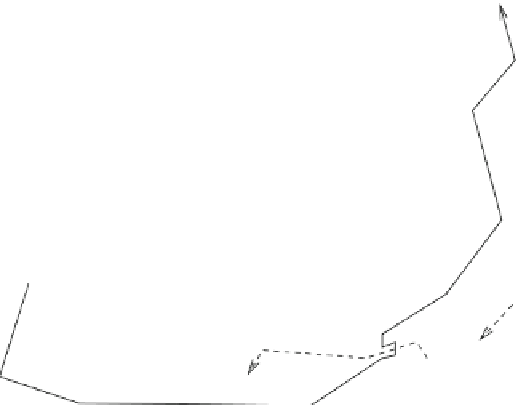
Fig. 9.8
Biochemical pathways stimulated by applied pressure and shear (Sources: [
1058
-
1060
]).
Initiation is done via: (1) ion channels; (2) growth factor receptors and others Tyr kinase receptors
(RTK); (3) G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR); (4) membrane NADH/NADPH oxidase (NOx);
and (5) adhesion molecules, mainly integrins, but also cadherin-5 and IgCAMs. Effectors include
small GTPases, PI3K, PKB, PKC, NO, FAKs, TGF, and O
2
). Main targets are the
transcription factors for cell and tissue remodeling (with possible degradation via MMPs after
a long-duration pressure rise), such as NF
(O2
−
κ
B, the cytoskeleton, adhesion molecules, and ion
channels.
(4) membrane rafts (caveolae); and (5) stress-sensitive enzymes connected to the
plasma membrane. Stimulated mechanosensors initiate different signaling pathways
to trigger responses.
Mechanotransduction generally occurs at numerous sites at the plasma
membrane and eventually inside the cell because mechanical stresses are
transmitted to multiple cellular structures, especially via the cytoskeleton on
load-bearing molecules. All agents involved in mechanotransduction then act
synergistically. Plasmalemmal, cytoskeletal, and nuclear scaffold proteins serve
as mechanotransmitters.
9.10.1.1
Plasmalemmal Receptors and Carriers
The density in pressure-activated cation channels increases in endothelium
subjected to high pressure, with complete reversal by antihypertensive ther-
apy
[
1061
].
Mechanosensitive
potassium
channels
modulate
plasmalemmal



















































































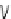





Search WWH ::

Custom Search