Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 2.2
Endosteal niche of
hematopoietic stem cells.
Interactions between
hematopoietic stem cells and
osteoblasts
(Sources: [
56
,
60
]).
N−cadherins
HSC
Ang1
Tie2
Notch1
Jagged1
osteoblast
CaR
osteopontin
Ca
bound stem cell factor
19
and its receptor SCFR, as well as CXCR4 can mediate their
sequestration in the niche [
62
].
Osteoblasts secrete multiple cytokines that promote the proliferation of
hematopoietic cells. Specialized spindle-shaped N-cadherin-expressing osteoblasts
of the endosteum directly contact hematopoietic cells via N-cadherin.
20
Many
stromal cell lines of endosteal bone surfaces that are involved in bone modeling,
are required in HSC maintenance. The endosteal niche can contain quiescent and
self-renewing hematopoietic stem cells.
Osteopontin
that prevents the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells may
maintain HSC quiescence (Fig.
2.2
).
Angiopoietin-1
at the osteoblast surface
interacts with its receptor Tyr kinase with Ig and EGF homology domains TIE2
on stem cells to maintain stem cell quiescence in the niche.
Certain situations such as inflammation trigger the activity of osteoclasts along
the stem cell niche, secretion of enzymes (cathepsin-G, elastase, MMP9, etc.)
and cytokines (interleukin-8), and mobilization of progenitors from the bone
marrow to the circulation [
63
]. Osteoclasts require TNFSF11 from osteoblasts for
proliferation and bone resorption. Activating osteoclasts via either TNFSF11 or
other stimuli leads to emigration of hematopoietic stem cells into the circulation.
On the other hand, increased osteoblast activity via parathyroid hormone receptor
or inactivation of the bone morphogenic protein receptor-1A causes a proliferation
of hematopoietic stem cells.
19
A.k.a. hematopoietic growth factor and steel factor (SLF).
20
Receptor Tyr kinases TIE1 and TIE2 are required in HSC maintainance in HSC microenviron-
ment. Receptor TIE2 activated by angiopoietin-1 secreted by osteoblasts upregulates N-cadherin
expression in hematopoietic stem cells and maintains HSC quiescence via CKI1a cyclin-dependent
kinase inhibitor.







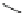





Search WWH ::

Custom Search