Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
PL
aCoAS
CytP450 epoxygenases
EET
sEH
AA
DHET
PLA2
EC
PL
EET
DHET
K
3Na
SMC
VGCC
VGCC
CaKC
NaKATPase
−
Ca
2K
Ca
hyperpolarization
−
−
20−HETE
relaxation
contraction
AA
CytP450
ω
hydroxylase
PLA2
PL
Fig. 8.4
Cytochrome-P450 (CytP450) synthesizes vasoactive metabolites of arachidonic acid
(AA;
Source:
[
822
]).
Activated
by
endothelin-1
or
angiotensin-2
receptor,
phospholipase-
A2
releases
arachidonic
acid
from
plasmalemmal
phospholipids
(PL).
Eicosanoids,
such
as
epoxyeicosatrienoic
acids
(EET)
produced
by
cytochrome-P450
epoxygenase
and
20-
hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (20HETE) by
-hydroxylase, regulate blood pressure. Soluble
epoxide hydrolase (sEH) catalyzes the conversion of EETs into dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids
(DHET). Conversely, EETs are incorporated into plasmalemmal phospholipids by acyl coenzyme-
A synthase (aCoAS). Potential of the intracellular edge of the plasma membrane is negative with
respect to that of the extracellular face. Agent 20HETE produced by smooth myocytes (SMC)
is a vasoconstrictor that hampers the activity of Ca
2
+
-activated K
+
channels (CaKC) and Na
+
-
K
+
ATPase, thus preventing K
+
and Na
+
efflux that causes cell depolarization to activate Ca
V
1
channels and elicit SMC contraction. Agents EETs and DHET released by endothelial cells (EC)
activate Ca
2
+
-activated K
+
channels of SMC sarcolemma, hence provoking a K
+
efflux and cell
hyperpolarization that inhibits Ca
2
+
influx via voltage-gated Ca
2
+
channels (VGCC or Ca
V
),
leading to SMC relaxation.
ω
In endothelial cells, cytochrome-P450 epoxygenase causes, independently of
nitric oxide and prostacyclin, vasodilation of several vascular beds, particularly
in the heart and kidney, by the production and release of epoxyeicosatrienoic and
dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (Fig.
8.4
).




























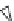










Search WWH ::

Custom Search