Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Ca
EC
A
GJ
TJ
IP3
EC
PC
PGE2
N
Ca
Glu
COx1
PLA2
N
A
EC
IP3
A
Ca
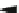
Fig. 7.6
Interactions between neurons (N), astrocytes (A), pericytes (PC), and endothelial cells
(EC) for functional hyperemia (TJ: tight junction, GJ: gap junction; Source: [
675
]). With their
extensions to both the vasculature and the nerves, astrocytes are anatomical links between the
circulatory and nervous systems. Induced vasodilation involves cyclooxygenase COx1, and inositol
trisphosphate (IP
3
).
7.4.4
Drug Delivery
The blood-brain barrier prevents the delivery of most therapeutic molecules to
their targets within the brain parenchyma, such as neurons and glial cells. A
solution for large molecules consists of triggering transcytosis via cell receptors
of the blood-brain barrier (low-density lipoprotein receptor, transferrin receptor,
insulin-like growth factor receptor) that bind ligands to facilitate their transport to
the central nervous system by adding the receptor-binding domain of the targeted
ligand (so-called molecular Trojan horses) [
677
]. A non-replicating lentivirus vector
system is used to deliver a substance to neurons and astrocytes by fusing it to the
binding domain of ApoB for low-density lipoprotein receptor and adding a secretory
sequence to allow its release. Such a method provides a source (from either a central
or peripheral organ, such as liver, spleen, or muscle, in the cells of which genes
are introduced) for prolonged production and release in the blood flow of a BBB-
crossing drug, but fusion proteins must be immunocompatible.


















Search WWH ::

Custom Search