Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CA
GRK
−
cytokine R
ErbB2/3/4
IGF1R
β
AR
GPCR
Gs
cAMP
PKA
RC
VDCC
RC
JaK
Ca
MAP3K
Ca
CamK2
SR
SR
SERCA
PLb
PLb
SERCA
MAP2K
Ca
STAT
PDE5A
calpain3
PI3K
calcineurin
myosin
MAPK
titin
T−Cap
MLP
actin
PAK1
PKB
sarcomere
PP2A
M
Z
Z
PKC
genes
NF
κ
B
nucleus
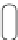
Fig. 5.14
Cytokine receptors, HERs, and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) activate
the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JaK-STAT) pathway, mitogen-
activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-protein kinase-B
(PI3K-PKB) pathway, to regulate gene expression (Source: [
416
]). Calcium-activated PP3 (cal-
cineurin) dephosphorylates NFAT transcription factors involved in cardiac remodeling. Mechanical
stresses stimulate Z-disc sensors. The titin-telethonin-muscle-specific LIM protein (MLP) sensor
binds PP3 for mechanotransduction. Excitation-contraction coupling requires calcium ions.
Calcium fluxes govern myofilament contraction and relaxation, particularly via Ca
V
1.2, or L-type
voltage-dependent calcium channel (VDCC), ryanodine channel (RC), and sarcoplasmic reticulum
calcium ATPase (SERCA) associated with its inhibitor phospholamban (PLb). The activity of these
3 calcium channels is regulated by protein kinase-A (PKA) and calcium-calmodulin-dependent
kinase-2 (CamK2). PKA is stimulated by G-protein-coupled receptors, such as the
β
-adrenergic
receptor (
β
AR). Protein kinase PKC
(PKC), located at the Z disc, regulates cardiomyocyte
contractility and hypertrophy. p21-Activated kinase-1 (PAK1) interacts with protein phosphatase-
2A (PP2A), targeting troponin-I and enhancing calcium sensitivity. Calpain-3 activates NF
κ
B.
Phosphodiesterase-5A (PDE5A) dissociates from the Z disc during heart failure. In heart failure,
GRK2 desensitizes G-protein activation of ACase.




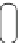


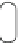





















































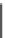


Search WWH ::

Custom Search