Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CA
ANP
BNP
neuroregulin
EGF
IGF1
ET1
FGF
TGF
TNF
ATn2
stress
FGFR
RTK
TGFR
TNFR
GPCR
GC
Ras
Rac Rho
PLC
MAP4K
MAP3K
NIK
PI3K
TAK1
cGMP
ROS
DAG
PP3
Raf
MAP3K
IKK
PDK1
IP3
PKG
MAP2K4/
7
MAP2K3/6
MAP2K1/
2
MAP2K5
PKC
Ca
PKB
JNK
p38
ERK1/2
ERK5
PKD
Cam
JNKPase
GSK3
mTOR
NFAT
CamK
NFκΒ
cFlIP
antioxydants
transcription factors
nucleus
NFAT
HDAC
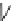
Fig. 5.13
Signaling pathways that initiate the cardiac hypertrophy (Source: [
411
]). Signaling
starts at the sarcolemma by ligands (natriuretic peptides ANP and BNP, angiotensin-2 [ATn2],
endothelin-1 [ET1], fibroblast growth factor [FGF], epidermal growth factor [EGF], insulin-
like growth factor-1 [IGF1], transforming growth factor-
α
[TNF]) that bind to receptors (G-protein-coupled receptors [GPCR] and receptor Tyr kinases
[RTK]), activating cytosolic effectors (guanylate cyclase-A [GC]; protein kinases [PKB, PKC,
PKD, and PKG]; phospholipases [PLA2 and PLC]; mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways
[MAP4K, MAP3K, Raf, MAP2K, ERK, JNK, and P38MAPK]; small GTPases [Ras, Rac, and
Rho]; diacylglycerol [DAG] and inositol trisphosphate [IP
3
]; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase [PI3K];
phosphoinositide-dependent kinase [PDK]; glycogen synthase kinase-3
β
[TGF], and tumor-necrosis factor-
[GSK3]; calmodulin-
dependent kinase [CamK]; target of rapamycin [TOR]; nuclear factor of activated T-cells [NFAT];
NF
κ
B-inducing kinase [NIK]; inhibitor of NF
κ
B kinase [IKK]; and cyclin-dependent kinase), then
transcription factors (nuclear factor-
κ
B[NF
κ
B], and nuclear factor of activated T-cells [NFAT]),
and nuclear components (histone deacetylases [HDAC]). NF
κ
B impedes prolonged JNK signaling
induced by TNF
α
via anti-oxidants and cellular flice-inhibitory protein (cFlIP), thus subsequent
apoptosis. Transient MAPK stimulation by TNF
α
favors cell growth.
β
Catecholamines, angiotensin-2, and endothelin-1 bind to specific G-protein-
coupled receptors (
1-adrenoceptor and angiotensin-2 and endothelin receptors) of
the cardiomyocyte sarcolemma (Fig.
5.13
)[
411
].
α






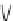

























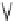
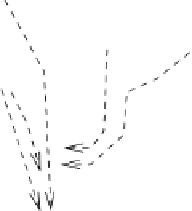





































Search WWH ::

Custom Search