Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
GPCR
Gq
Ras
Raf1
MAP2K2
ERK2
FHL1
N2B
stretch sensor
titin
nucleus
cardiac hypertrophy
gene expression
Fig. 5.12
Cardiomyocyte stretch sensor and signaling (Source: [
408
]). Protein FHL1 is associated
with titin N2b subsegment in the sarcomere and serves as scaffold protein for the Raf1-MAP2K2-
ERK2 module downstream from G
α
q stimulation.
5.8.1
Mechanotransduction in CMC Hypertrophy
Mechanical stresses are sensed by cardiomyocyte sarcomeres and transduced to
generate hypertrophy. Dysfunction of these pathways leads to maladaptive hyper-
trophy. Although cardiac adaptive hypertrophy allows an increase in myocardial
contractility, initially compensatory, sustained hypertrophy indeed serves as an
index for cardiac morbidity and mortality.
Cytoskeletal proteins of the LIM domain-containing protein family intervene in
myocyte response to mechanical stress. Four-and-a-half LIM domain-containing
proteins (FHL1-FHL3) have multiple binding partners. They are involved in striated
myocyte development and function.
Protein FHL1 is the single FHL member that is upregulated in mouse heart
subjected to hypertrophic excitation. In humans, FHL1 level is strongly increased in
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Protein FHL1 belongs to the complex of cardiomy-
ocyte sarcomere that senses mechanical stress via the cardiac-specific N2b stretch
sensor domain of sarcomeric titin within the sarcomeric I band [
408
]. Titin N2b
subsegment contributes to myofibrillar passive tension generated upon active stretch
imposed by the sarcome during systole that is used for diastolic relaxation. Scaffold
FHL1 connects to myocyte stretch sensor at titin N2b region to the Gq-cRaf-
MAP2K2-ERK2 cascade (Fig.
5.12
). It not only determines subcellular location
of MAPK module, but also enhances intensity and duration of MAPK hypertrophic
signaling.
Cardiomyocytes detect deformation possibly via plasmalemmal integrins and
their partners, such as melusin (or Itg
β
1BP2), and cardiac (muscle)-specific LIM

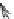











Search WWH ::

Custom Search