Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
PCr
Cr + PO4
ATP
AMP
energy for
(1) synthesis and growth
(2) molecule import and export
(3) electrochemical wave conduction
(4) contraction
AMPK
ERR
α
PPAR
α
PGC1α
6PF(2)K
F(2,6)P2
TFAm
NRF1/2
glycolysis
PFK
fatty acid oxydation
gene transcription
Glc
mitochondrial gene expression
Fig. 5.11
Energy supply and reserve in cardiomyocytes. At rest, fatty acid oxidation covers most
of energy need and the remainder comes from oxidation of carbohydrates, principally glucose.
When heart activity rises, additional sources of ATP synthesis such as phosphotransferase reactions
catalyzed by creatine kinase (CK) are involved. ATP production by phosphotransferase reactions
is about 10 times faster than ATP synthesis in mitochondria. Phosphocreatine (PCr) actually is the
primary energy reserve element in cardiomyocytes. Glycolysis is the set of reactions that converts
glucose (Glc) into pyruvate. Phosphofructokinase (PFK) that controls glycolysis is stimulated by
AMP and fructose (2,6)bisphosphate (F(2,6)P2). Attenuated phosphocreatine concentration and el-
evated AMP level activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) that increases glucose transport
by upregulating transporter GluT4 expression and activates PFK by stimulating 6-phosphofructo
2-kinase (6PF(2)K) activity. Kinase AMPK also activates mitochondrial estrogen-related receptor
ERR
that regulates fatty
acid oxidation. ERR
α
,ERR
β
,andERR
γ
regulate cardiac energy metabolism. Factor PGC1
α
stimulates mitochondrial genesis, as it increases the production of nuclear respiratory factors
NRF1 and NRF2 that regulate mitochondrial transcription factor-A TFAm and ERR
α
(NR3b1) that
coordinates the expression of genes encoding mitochondrial proteins. Moreover, PGC1
α
regulates
the expression of genes encoding proteins involved in fatty-acid oxidation via coactivation of
PPAR
α
and ERR
α
.
α
and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-
γ
coactivator PGC1
α
Phosphocreatine (Vol. 1 - Chap. 4. Cell Structure and Function) is the primary
energy reserve element in cardiomyocytes. Production of ATP by creatine kinase is
about 10 times faster than ATP synthesis in mitochondria, which is approximately
20 times quicker than ATP generation via glycolysis.
Glycolysis is the set of reactions that converts glucose (Glc) into pyruvate.
Glycolysis in aerobic condition is the prelude of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and
mitochondrial electron transport chain, where most of the free energy in glucose is
harvested. Consumption of ATP is a preamble to ATP synthesis. Phosphofructoki-
nase (PFK) is the most important controller in glycolysis. It is inhibited by high ATP
level and stimulated by AMP and fructose (2,6)-bisphosphate (F(2,6)P
2
). Attenuated












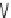

















Search WWH ::

Custom Search