Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
myosin
LMM
(tail)
HMM
(head)
S1
(binding site)
S2
(rod)
actin−myosin cross bridge
−
ATP
−
myosin binding site
actin
+
tropomyosin
+
troponin complex
TnT
Ca
−
TnI
TnC
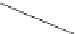
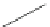
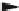
Fig. 5.7
Actin and myosin filaments. The thick filament is composed of many myosin units lined
up in a bidirectional arrangement, each unit being made of 2 myosin chains wrapped around each
other like a twisted golf club. The combination of calcium ions to troponin-C (TnC) that liberates
the myosin-binding site on actin, followed by the inactivation of the tropomyosin-troponin
complex, allows myosin head displacement and actin sliding. The heterotrimeric troponin complex
is formed by regulatory troponin-C, inhibitory troponin-I (TnI), and tropomyosin-binding troponin-
T (TnT). It is positioned along the actin filament at every seventh actin monomer. Troponin-C
and calmodulin are the main targets of calcium ions. Both TnC and Cam contain 4 Ca
2
+
-binding
domains. Calcium binding to the regulatory site of the cardiac troponin-C (cTnC) affects both
its interaction with TnI and the interaction of TnI with TnT and tropomyosin. In the absence of
Ca
2
+
, TnI inhibits the interaction of myosin-2 with actin. Ca
2
+
binding to cTnC relieves the TnI
inhibition, ensuring contraction. Ca
2
+
-induced conformational changes of troponin-C are imparted
to all actin monomers via TnI and TnT acting via 2 tropomyosin threads on both sides along the
entire actin filament. cTnI phosphorylation by either PKA or PKC lowers the TnC affinity for
calcium ions (positive lusitropy). Two main mechanisms change contractibility: (1) modifications
in the amplitude and/or duration of transient Ca
2
+
fluxes and (2) modifications in the sensitivity of
the contractile filaments to calcium by phosphorylation of the myosin light chain and/or troponin-I.
Moreover, sarcomere compression due to stretching associated with rising diastolic filling brings
the contractile filaments closer together, thus facilitating actin-myosin interaction and increasing
the TnC affinity for calcium.








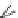
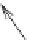







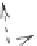


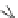
Search WWH ::

Custom Search