Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
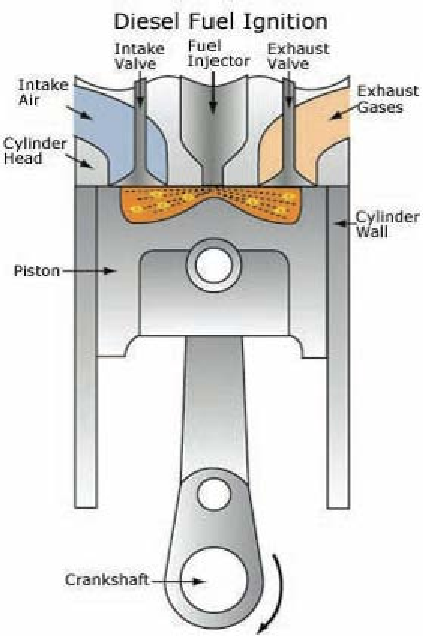
Figure 15. The diesel engine, invented by Rudolf Diesel in 1894 and characterized by its ignition of
hydrocarbon fuels by compression with heated air, rather than by ignition with an electrical spark [41].
2. State of the Science
2.1. Feedstocks and Coproducts
An important challenge faced by biodiesel in competing with petroleum diesel is the
comparatively high price of its plant oil feedstocks. In June, 2004, diesel prices ranged from
$1.50 per gallon in Oklahoma to $2.20 per gallon in Seattle, Washington [9], while the cost of
soybean oil, the primary biodiesel feedstock in the United States, was reported at $2.19 per
gallon (27.34 cents per lpound) before conversion to biodiesel even occurred [10].
The margin is narrowing, however (in May 2005, diesel prices ranged from $1.98 per
gallon in Knoxville, Tennessee to $2.53 per gallon in Seattle, Washington [11], while the cost
of soybean oil dropped to 22.31 cents per pound [12]), and on April 25, 2005, Blue Sun 100
percent pure biodiesel (B100) reached a low of $2.39 per gallon in Denver, Colorado,
compared to local petroleum diesel prices of $2.29 per gallon (www.boulderbiodiesel.org).
In addition, tax incentives are becoming popular internationally as governments attempt
to reduce their dependence on foreign oil. Even in the United States, which has traditionally
subsidized petroleum use substantially in comparison to Europe (diesel fuel cost is greater by
a factor of 1.5-2.5 across Europe [13]), bills have been recently introduced to extend the