Database Reference
In-Depth Information
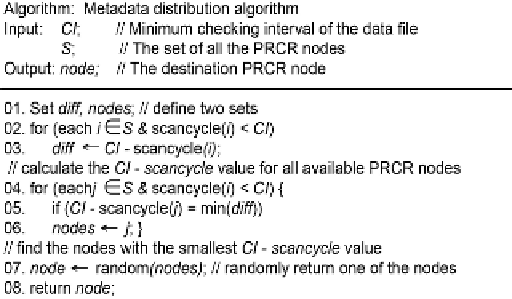
Figure 6.4 Pseudo code of metadata distribution algorithm
addition to the algorithm, to distribute metadata, there are several issues that need to
be further addressed.
•
First, the capacity of each PRCR node is limited; when more and more data files are man-
aged by PRCR, the capacity of PRCR nodes could gradually run out. To address this issue,
the independence of each PRCR node has provided great elasticity to the organization of
PRCR. When one of the PRCR nodes is reaching or about to reach its maximized capacity,
a new PRCR node is created, where the time for the scan cycle of the new PRCR node can
be set to the same as the fully occupied PRCR node, which should be considered according
to the data management requirement.
•
Second, the data reliability model with a variable disk failure rate has led to the side effect
that there exist multiple checking interval values for each data file, that is, the checking
interval changes from time to time. Once the checking interval increases to a threshold that
is equal to the scan cycle of another PRCR node, current metadata distribution becomes
sub-optimal. To address this issue, several solutions could be applied. For example, the scan
cycles of PRCR nodes need to be well organized so that each data file is managed by the
PRCR node with a scan cycle smaller than all the checking interval values that the data files
could have. Or, if the metadata of data files need to be redistributed no matter how, the redis-
tribution could be conducted in a batch mode to reduce its impact and computation overhead.
•
Third, the metadata are distributed according to the calculation of the minimum replication
algorithm. However, the predicted storage duration could be different from that of the disks
in reality, and hence prediction errors could occur. Such a situation is most likely caused by
the deviation of disk failure rates, and the only type of error that could possibly jeopardize
data reliability is that the disk failure rates are being underestimated, so that the checking
interval is overestimated. In general, the situation of prediction errors is very similar to the
second issue. Therefore, the solutions for the second issue are also applicable to prediction
errors. In addition, the disk failure rates can be adjusted by statistics on the disks and so forth.
6.5
Evaluation of PRCR
Based on the results of several experiments conducted on both a local computer and
Amazon Web Services (AWS), in this section we evaluate PRCR from the aspects of
performance and cost-effectiveness.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search