Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
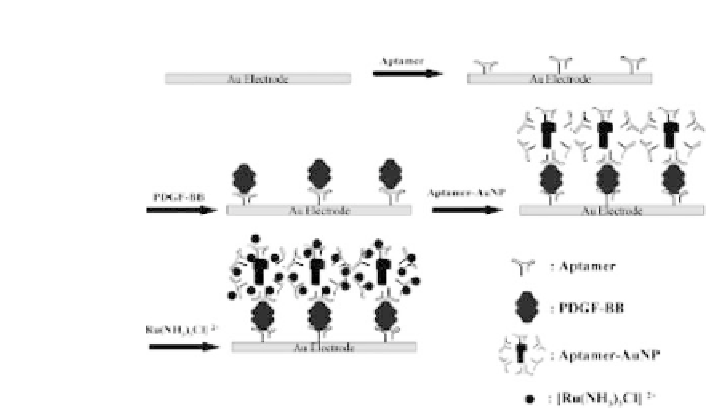
Figure 2.6.
Schematic representation of the electrochemical aptasensor
basedonasandwichassayandontheuseof[Ru(NH
3
)
5
Cl]
2
+
asredoxprobe.
Table2.1. ExamplesofAptamer-BasedElectrochemicalBiosensorsBased
on the Use of Fe(CN)
3
−
/
4
−
6
as Redox Probe
Target
ElectrochemicalTechnique AnalyticalCharacteristics
References
Oxytetracycline Cyclic voltammetrySquare DL 5 nM Range 1-100 nM
Kim
et al.
(2009)
wave voltammetry
17b-estradiol
Cyclic voltammetrySquare Linear range0.01-1 nM
Kim
et al.
(2007)
wave voltammetry
Thrombin
Impedancespectroscopy
Range 0.5-500 nM
Lee
et al.
(2008)
DL 6
×
10
3
cells/mL
Cancer cells
Impedancespectroscopy
Pan
et al.
(2009)
Thrombin
Impedancespectroscopy
DL 0.01 nM Range1-50 nM Zhang
et al.
(2009)
Adenosine
Cyclic voltammetry
DL 1 nM Range 0.1-100 nM Zheng
et al.
(2008)
Adenosine
Impedancespectroscopy
DL 0.1 nM
LI
et al.
(2007)
Cocaine
Impedancespectroscopy
DL 5 nM
Elbaz
et al.
(2008)
AMP
Impedancespectroscopy
DL 10 nM
Elbaz
et al.
(2008)
due to the presence of [Fe(CN)
3
6]
in solution. A decrease in current
was evident after the binding of oxytetracycline to the aptamer: this
wasprobablyduetothechangesintheconformationoftheaptamer
which caused changes in permeability and in charges on the elec-
trode. The biosensor could detect oxytetracycline in the range 1
to 100 nM with high specificity since negligible interference was
presentwhenanalyzingstructurallysimilarantibioticssuchasdoxy-
cyclineand tetracycline.