Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
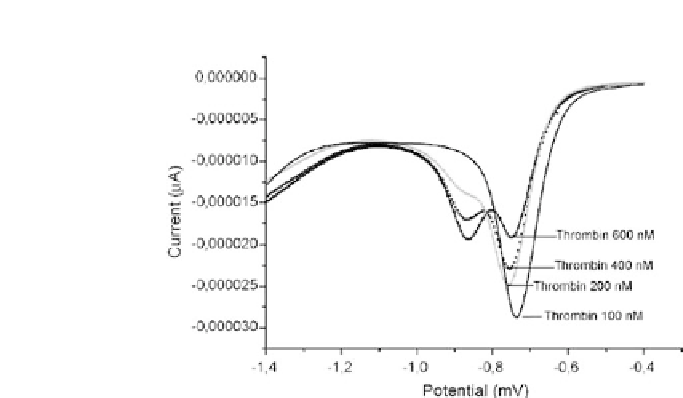
Figure 2.3.
DPV scans of the thrombin substrate (
β
-Ala-Gly-Arg-
p
-
nitroaniline) solutions incubated with aptamer-thrombin modified beads.
Different concentrations of thrombin in the concentration range 100 to
600nMwereincubatedwiththeaptamer-modifiedbeads,whileafixedcon-
centration of thrombin substrate was used (200
μ
M). The thrombin sub-
strate and the
p
-nitroaniline released during hydrolysis showed different
redox potentials (the DPV peak potential of
β
-Ala-Gly-Arg-
p
-nitroaniline
−
was
730 mV vs. Ag/AgCl pseudo-reference electrode, whereas the
released
p
-nitroaniline peak potential was
−
870mV vs. Ag/AgCl pseudo-
reference electrode).
2.6 Electrochemical Metal Nanoparticle-Labeled
Aptasensors
The use of NP labels is a strategy relatively new in the develop-
mentofelectrochemicalaptasensors.Thelabelsusedareessentially
metallic NPs or inorganic (semiconductor) nanocrystals [22-25].
They allow developing elegant strategies for interfacing aptamer-
target analyte recognitioneventswithelectrochemical transduction
amplifyingtheresultingelectricalresponseandthusgivingrisetoan
improvement of the assay sensitivity. In particular, the redox prop-
erties of gold NPs have made possible their widespread use as elec-
trochemical labels in aptasensor development [24]. Most of these
strategies involve a stripping measurement of the metal tag: metal
NPs can be oxidized to form the corresponding metal ions that can
bethen detected electrochemically.