Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
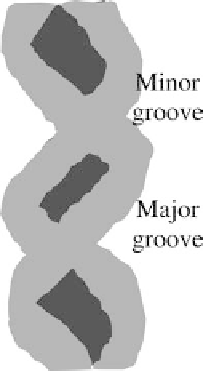
Figure 16.8.
Minorand major grooves.
There are three different forms of DNA. B-form DNA also called
Watson-Crick structure is formed by two individual DNA strands
aligned in an antiparallel manner. B-form is the most stable form of
DNA molecule under physiological conditions. It is long, thin, and
right-handed. The number of base pairs per helical turn is 10.5.
B-DNA has wide major groove and narrow minor groove. A-form
DNA is also right handed, but the helix is shorter and wider than
B-form.Thereare11basepairspereachhelicalturnofA-formDNA.
The major groove of A-DNA is deeper and thus the minor groove is
shallower. The present of A-DNA in cells is uncertain. Alternating
runs of (CG)n
·
(CG)n or (TG)n
·
(CA)n dinucleotides in DNA under
superhelicaltensionorhighsaltcanadoptaleft-handedhelixcalled
Z-DNA. In this form, the two DNA strands become wrapped in a
left-handed helix, which is the opposite sense to that of canonical
B-DNA. The number of base pairs per helical turn is 12 in Z-form.
The structure is thinner and longer. While the minor groove of Z-
form is deep, its major groove is hardly apparent. There are some
prokaryotic and eukaryotic examples for Z-form DNA. It has been
suggested that Z-form DNA functions in genetic recombination or
regulation of somegenes' expression.
In addition to the specificity of the hydrogen bonding between
complementary bases, unwounding and rewounding of the double