Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
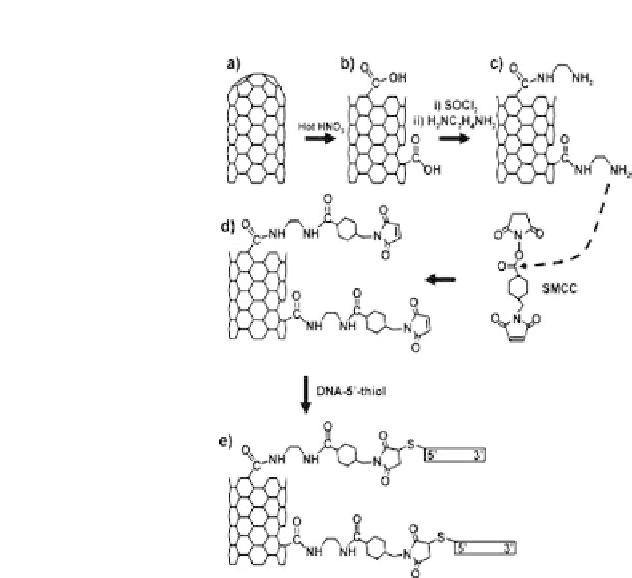
Figure 14.16.
Scheme for fabrication of covalently linked DNA-nanotube
adducts.
of amine functionalized DNA to oxidized SWCNTs in solution was
demonstrated [96].
However, Cai
et al.
[86] were the first to demonstrate the
use of CNTs in an electrochemical DNA biosensor fabricated by
covalently immobilizing a DNA probe onto a MWCNT-modified
glassy carbon electrode and detecting the hybridization of target
DNA by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) using an electroactive
intercalator, daunomycin, as an indicator, illustrated in Fig. 14.17.
The MWCNTs served as a method of covalent attachment of probe
DNA, butalso improved the sensitivity of thiselectrochemical assay.
A detection limit of 1.0
×
10
-
10
M was achieved whereas previous
results reported by Marrazza
et al.
[97] using similar experiments
with the probe DNA directly attached to nonmodified carbon
electrodes gave a detection limit of 1
g/ml of target sequence. The
use of MWCNTs led to an increased rate of heterogeneous electron
μ