Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
as electroactive labels. Amperometric currents were generated
from the Pt-catalyzed reduction of H
2
O
2
following DNA target
capture onto a DNA-probe mixed monolayer gold electrode and
secondary DNA-Pt nanoparticle hybridization with a detection limit
of 10 pM for target DNA. The substitution of an enzyme with an
inorganic nanoparticle combines the advantages of high sensitivity
from substrate turnover and increased stability for the amplified
detection of biomolecules. Yang and coworkers [38] described the
detection of DNA hybridization onto an ITO electrode using DNA-
conjugated gold nanoparticles to catalytically oxidize hydrazine.
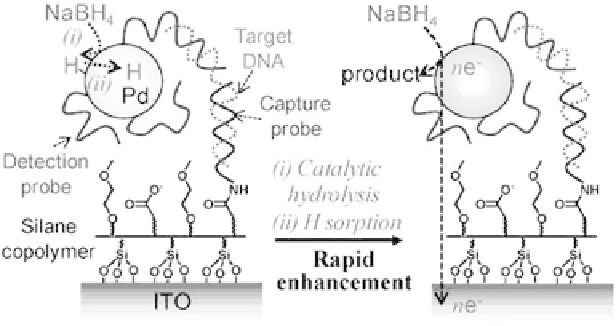
Becauseofthehighoverpotentialandslowelectrontransferkinetics
of hydrazine oxidation, a NaBH
4
treatment was used to enhance
the catalytic signals to produce a detection limit of 1 fM. The
pre-treatment hydrolyzed NaBH
4
and induced sorption of atomic
hydrogen onto the gold nanoparticles. This process, however,
occurred at very slow rates at higher pH. The substitution of
gold nanoparticles with Pd nanoparticles increased the catalytic
hydrolysis time, even at high pH, and allowed the construction of
a DNA hybridization detector using the Pd catalyzed oxidation of
NaBH
4
, shown in Fig. 14.7. ITO electrodes were modified using
silanization with a copolymer containing carboxylic acid groups (to
Figure 14.7.
Schematic view of DNA detection using the catalytic and
electrocatalytic oxidation of NaBH
4
on Pd NPs and the rapid enhancement
of electrocatalytic activity of DNA-conjugated Pd NPs.