Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
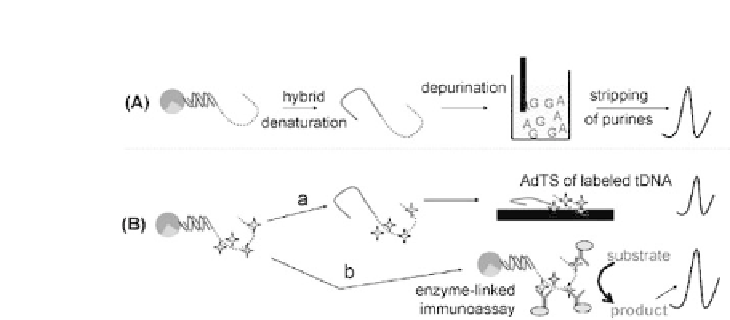
Figure 14.2.
Some detection principles used in the double-surface DNA
hybridization techniques. (A) Label-free detection of target DNA (tDNA).
(B) Labeling of tDNA. Redox labels are covalently attached to the tDNA
strandoutsidethesegmentoronasecondaryDNAstrandrecognizedbythe
captureprobe.Afterhybridizationandseparation,theelectroactivetagsare
determined electrochemically (e.g., by
ex situ
adsorptive stripping voltam-
metry (a). Alternatively, electrochemical enzyme-linked immunoassay can
be used for detection of labeled tDNA at the MB surface (b).
allow for a higher degree of hybridization e
ciency than DNA
probes immobilizedon a flat substrate.
Figure 14.2 shows some general schemes where magnetic
particle-based DNA assays have been reported using a variety of
detection schemes utilizing two surface detection techniques. For
instance,alabel-freeapproachhasbeendevelopedwhereafterDNA
hybridization and magnetic separation the target molecule can be
detectedbycathodicstrippingofnucleicacidbases(Fig.14.2A)[11].
This approach can be applied directly; for instance, measuring gua-
nine oxidation with inosine-substituted DNA probes to lower back-
groundsignalsfromguaninescontainedintheprobestrand[12],or
byreleasingpurinebasesbyacidtreatmentforsub-nanomolarDNA
detection at silver, copper, platinum, or gold amalgam electrodes
[13-15]. The accumulation of guanine and adenine anodic signals
at carbon electrodes through a Cu(I)-purine complex can also be
used for an amplification effect. Alternatively, the labeling of tDNA,
or the corresponding secondary reporter probe in a “sandwich”
hybridization assay can be performed on magnetic particles as
showninFig.14.2B.Redoxlabels,suchascovalentlyboundosmium