Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
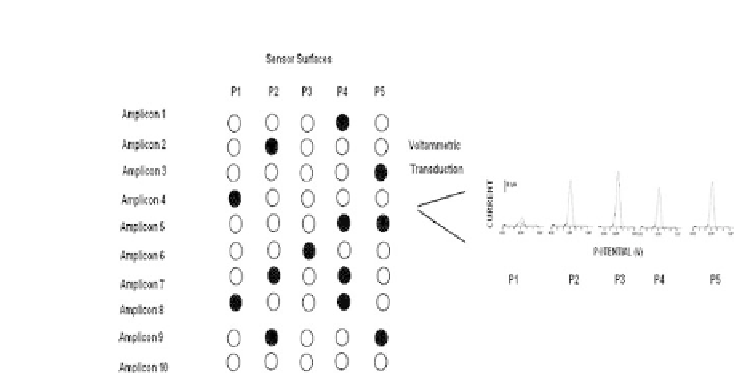
Figure 13.6.
Schematic presentation of electrochemical genosensing of
multiple point mutationsin PCRamplicon.
the 81-bp hotspot region between the 507th and 533rd codons
of the rpoB gene. Five different inosine-modified capture probes
represented several parts of rpoB gene area including several
SNPs were immobilized onto electrode surfaces. Hybridization
and mismatch detection was performed by monitoring guanine
oxidation. In conclusion, rapid, cost-effective, highly sensitive, and
sequence-specific array system which is capable of multiple SNP
detection at the same time was developed. This method was able to
detect down to 18.65 fmol/mL. Figure 13.6 represents detection of
multiple point mutations in mycobacterium tuberculosis amplicons
based on label-free electrochemical genosensing. Five capture
probes (P1, P2, P3, P4, P5) representing several parts of amplicon
were immobilized onto different sensing areas. After hybridization
with an amplicon, different responses of guanine oxidations were
obtaineddue to the region of the SNP.
13.4 Conclusion
Throughout this chapter, we demonstrated label-based and label-
free electrochemical genosensing techniques for the detection of
microbiological and inherited diseases devoted to clinical analysis.
The sensor technology is relatively cheap to produce, easily