Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
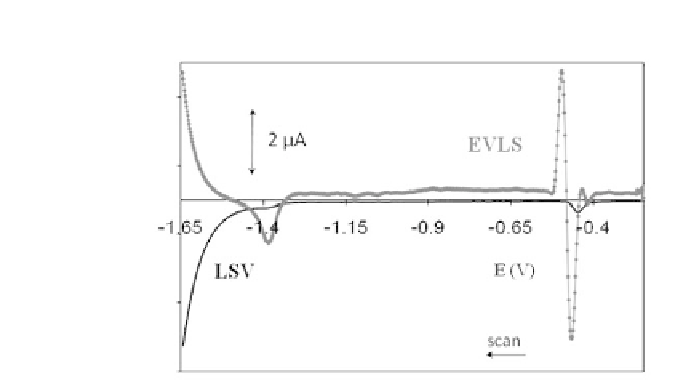
Figure 11.6.
AdS LSV and EVLS E4 of hydrolyzed adenosine on HMDE
in the presence of 20
μ
M Cu(II). Scan rates of 125, 250, and 500 mV/s
and potential step 5 mV. Reference current (black line) at a scan rate of
250 mV/s, accumulation time 120 s, accumulation potential -0.3 V, 0.1 M
acetate buffer, pH 5.1. Reproduced with permission from Jelen, F.,
et al
.,
Voltammetric study of adenine complex with copper on mercury electrode,
Electroanalysis
21
, 439 (2009). Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.
KGaA. See also Color Insert.
Results show that EVLS is a useful and sensitive tool not only for
bothqualitativeandquantitativemicroanalysisofadeninebymeans
ofCu(I)ionsbutalsoforrevealingdetailsincorrespondingelectrode
processes.
Voltammetric measurements confirm that Hg-modified carbon
electrodes are suitable for sensitive electrochemical detection of
ODNcomparedtomercuryelectrodes.Inthepresenceofthecopper
ions,theseelectrodesmodifiedbyamercurylayerwereusedforthe
detection of a picomolar quantity of ODN. The electrochemical step
includes a potential-controlled reduction of the copper ions Cu(II)
and accumulation of the Cu(I)-purine base residue complex on the
Hg-modified carbon surface. The proposed electrochemical method
can be used for the determination of different ODN lengths because
the stripping current peak of the electrochemically accumulated
Cu(I)-purinecomplexincreasedlinearlywiththelengthofODN.The
optical microscope images were used for the visualization of the
surface morphology of the bare and Hg-modified carbon electrodes
[64].