Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 11.2. Double EVLS functions eliminating two current compo-
nents
EVLS Function
Characteristics
Double EVLS Equations
E4
I
d
=
0;
I
k
=
0;
I
c
=
0
f
(
I
)
=
135
.
9
I
1
/
4
−
407
.
7
I
1
/
2
+
441
.
6
I
−
203
.
8
I
2
+
33
.
97
I
4
E5
I
d
=
0;
I
k
=
0;
I
c
=
0
f
(
I
)
=
46
.
63
I
1
/
4
−
112
.
6
I
1
/
2
+
100
.
9
I
−
.
80
I
2
+
.
39
5
830
I
4
I
d
=
0;
I
k
=
0;
I
c
=
=
.
31
I
1
/
4
−
.
60
I
1
/
2
+
.
E6
0
f
(
I
)
23
79
100
9
I
−
.
28
I
2
+
.
56
11
66
I
4
df(I)
I (μA)
EVLS
or
f
(
I
)
or
df
(
I
)
double EVLS
E (mV)
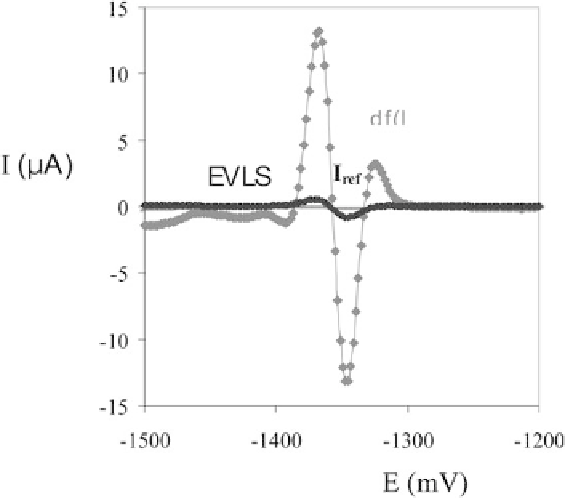
Figure 11.2.
Linear sweep (black), EVLS (blue), and double EVLS (red)
voltammograms of homo-ODN(dA
9
) inacetate buffer(pH5.3).d
f
(
I
)isthe
double elimination function E4 for simultaneous elimination of kinetic and
chargingcurrents,andconservingthediffusioncurrent.ScanratesforEVLS:
50, 100, 200, 400, and 800 mV/s, potential step 2 mV, reference scan 200
mV/s, time of accumulation 90 s, and potential of accumulation -100 mV
vs. Ag/AgCl/3M KCl. Reproduced with permission from Mikelova, R.,
et al.,
Double elimination voltammetry of short oligonucleotides,
Electroanalysis
19
, 1807 (2007). Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. See also
Color Insert.